A cardiac rehabilitation exercise program potentially inhibits progressive inflammation in patients with severe Chagas cardiomyopathy: A pilot single-arm clinical trial
- PMID: 32174990
- PMCID: PMC7053160
- DOI: 10.4103/jrms.JRMS_175_18
A cardiac rehabilitation exercise program potentially inhibits progressive inflammation in patients with severe Chagas cardiomyopathy: A pilot single-arm clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Cardiac rehabilitation exerts anti-inflammatory effect on several cardiovascular diseases; however, these effects were not described for Chagas cardiomyopathy, which is associated with pro-inflammatory imbalance.
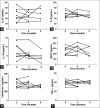
Materials and methods: Ten patients with severe Chagas cardiomyopathy performed 8 months of exercise training in a cardiac rehabilitation program. Interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β), IL-8, IL-10, interferon gamma (IF-γ), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) serum levels were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay at baseline, 4, and 8 months. The influence of exercise on cytokine levels was evaluated using the one-way analysis of variance for repeated measurements, with Bonferroni posttest for multiple comparisons.
Results: Levels of pro-inflammatory (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-8, IF-γ, and (MCP-1) and anti-inflammatory (IL-10) cytokines did not vary significantly during the observation period.
Conclusion: Exercise may benefit patients with severe Chagas cardiomyopathy by curbing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines in this disease characterized by a continuous state of inflammation.
Keywords: Cardiac rehabilitation; Chagas cardiomyopathy; cytokines; heart failure.
Copyright: © 2020 Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Talvani A, Rocha MO, Barcelos LS, Gomes YM, Ribeiro AL, Teixeira MM. Elevated concentrations of CCL2 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in chagasic cardiomyopathy. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;38:943–50. - PubMed
-
- Gleeson M, Bishop NC, Stensel DJ, Lindley MR, Mastana SS, Nimmo MA. The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise: Mechanisms and implications for the prevention and treatment of disease. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:607–15. - PubMed
-
- Mediano MF, Mendes Fde S, Pinto VL, Silva GM, Silva PS, Carneiro FM, et al. Cardiac rehabilitation program in patients with Chagas heart failure: A single-arm pilot study. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop. 2016;49:319–28. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
