Hepatitis B care pathway in Jordan: current situation, gaps and recommended actions
- PMID: 32175084
- PMCID: PMC7043903
- DOI: 10.1016/S2055-6640(20)30004-2
Hepatitis B care pathway in Jordan: current situation, gaps and recommended actions
Abstract
Objectives: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection remains a worldwide public health problem. The last major review of the HBV care pathway in the Middle East was published in 2011. This article aims to assess the current situation of the HBV care pathway in Jordan, identify gaps and barriers and recommend initiatives that could be taken to improve disease management across all stages of the care pathway.
Methods: A Delphi process was used between February and October 2017, including a literature review (PubMed and Google Scholar) for published articles on HBV in Jordan, followed by individual interviews with various healthcare professionals and group discussions with leading Jordanian hepatologists and gastroenterologists to provide context to the results of the literature review.
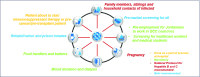
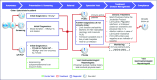
Results and discussion: The national prevalence of HBV is estimated to be around 2.4% and has declined from 9.9% in the pre-vaccination era. There is limited data on the burden of HBV-related hepatocellular carcinoma in the country. Awareness of various aspects of the disease is considered low among the general population and medium among primary care providers. There are several mandated national screening structures, however, established protocols for those that test positive and subsequent linkage-to-care are not optimal. In conclusion, significant improvements have been made in the past 30 years in Jordan in terms of decline in HBV prevalence. However, efforts must be made by all key stakeholders to optimise screening and linkage-to-care of patients and reduce both morbidity and mortality in the country.
Keywords: Jordan; awareness; diagnosis; epidemiology; hepatitis B; treatment.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Virus Eradication published by Mediscript.
Figures



References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 328 diseases and injuries for 195 countries, 1990-2016: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet 2017; 390( 10100): 1211– 1259. - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Global Hepatitis Report, 2017 . Available at: www.who.int/hepatitis/publications/global-hepatitis-report2017/en/ ( accessed November 2019).
-
- Specialist Panel on Chronic Hepatitis B in the Middle East A review of chronic hepatitis B epidemiology and management issues in selected countries in the Middle East. J Viral Hepat 2012; 19( 1): 9– 22. - PubMed
-
- WHO Hepatitis B Fact sheet. 2017. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-b ( accessed November 2019).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
