The current state of bionic limbs from the surgeon's viewpoint
- PMID: 32175092
- PMCID: PMC7047902
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.180038
The current state of bionic limbs from the surgeon's viewpoint
Abstract
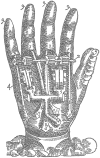
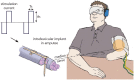
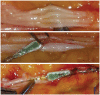
Amputations have a devastating impact on patients' health with consequent psychological distress, economic loss, difficult reintegration into society, and often low embodiment of standard prosthetic replacement.The main characteristic of bionic limbs is that they establish an interface between the biological residuum and an electronic device, providing not only motor control of prosthesis but also sensitive feedback.Bionic limbs can be classified into three main groups, according to the type of the tissue interfaced: nerve-transferred muscle interfacing (targeted muscular reinnervation), direct muscle interfacing and direct nerve interfacing.Targeted muscular reinnervation (TMR) involves the transfer of the remaining nerves of the amputated stump to the available muscles.With direct muscle interfacing, direct intramuscular implants record muscular contractions which are then wirelessly captured through a coil integrated in the socket to actuate prosthesis movement.The third group is the direct interfacing of the residual nerves using implantable electrodes that enable reception of electric signals from the prosthetic sensors. This can improve sensation in the phantom limb.The surgical procedure for electrode implantation consists of targeting the proximal nerve area, competently introducing, placing, and fixing the electrodes and cables, while retaining movement of the arm/leg and nerve, and avoiding excessive neural damage.Advantages of bionic limbs are: the improvement of sensation, improved reintegration/embodiment of the artificial limb, and better controllability. Cite this article: EFORT Open Rev 2020;5:65-72. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.180038.
Keywords: bionic limbs; limb amputation; prosthetics.
© 2020 The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
ICMJE Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest relevant to this work.
Figures

References
-
- Rang M. Amputations and prostheses in the story of orthopaedics. Philadelphia, London, Sydney, Toronto: WB Sounders Co., 2000:293–305.
-
- Ortiz-Catalan M, Håkansson B, Brånemark R. An osseointegrated human-machine gateway for long-term sensory feedback and motor control of artificial limbs. Sci Transl Med 2014;6:257re6. - PubMed
-
- Clement RGE, Bugler KE, Oliver CW. Bionic prosthetic hands: a review of present technology and future aspirations. Surgeon 2011;9:336–340. - PubMed
-
- Farina D, Aszmann O. Bionic limbs: clinical reality and academic promises. Sci Transl Med 2014;6:257ps12. - PubMed
-
- Raspopovic S, Petrini FM, Zelechowski M, Valle G. Framework for the development of neuroprostheses: from basic understanding by sciatic and median nerves models to bionic legs and hands. Proc IEEE 2017;105:34–49.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

