Fixation of AO-OTA 31-A1 and A2 trochanteric femur fractures using a sliding hip screw system: can we trust a two-hole side plate construct? A review of the literature
- PMID: 32175099
- PMCID: PMC7047904
- DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.190020
Fixation of AO-OTA 31-A1 and A2 trochanteric femur fractures using a sliding hip screw system: can we trust a two-hole side plate construct? A review of the literature
Abstract
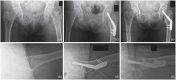
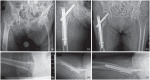
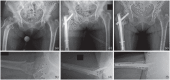
Trochanteric femur fractures are frequently fixed with a four-hole side plate sliding hip screw device, but in recent decades two-hole side plates have been used in an attempt to minimize operative time, surgical dissection, blood loss and post-operative pain.The aim of this review was to determine whether two-hole sliding hip screw constructs are an acceptable option for fixation of AO-OTA 31-A1 and A2 trochanteric femur fractures.An electronic MEDLINE® database search was performed using PubMed®, and articles were included in this review if they were reporting historical, biomechanical, clinical or outcome data on trochanteric fracture fixation using a two-hole sliding hip screw device.A two-hole dynamic hip screw with a minimally invasive muscle-splitting approach is recommended for fixation of AO-OTA 31-A1 simple trochanteric fractures; this implant is biomechanically safe, and allows the use of a minimally invasive muscle-splitting approach which potentially provides better clinical outcome, such as decreased surgical trauma, shorter operative time, less blood loss, decreased analgesics use, and shorter incision length. As the majority of reviewed publications relate to the dynamic hip screw, it is not clear whether the above recommendations can be extended to any other sliding hip screw device.An intramedullary device is recommended for all other extra-capsular proximal femoral fractures. Cite this article: EFORT Open Rev 2020;5:118-125. DOI: 10.1302/2058-5241.5.190020.
Keywords: dynamic hip screw; four holes; gliding hip screw; sliding hip screw; trochanteric femur fracture; two holes.
© 2020 The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
ICMJE Conflict of interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest relevant to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Results of intertrochanteric femur fractures treated with a 135-degree sliding screw with a two-hole side plate.J Orthop Trauma. 1999 Jan;13(1):5-8. doi: 10.1097/00005131-199901000-00002. J Orthop Trauma. 1999. PMID: 9892117
-
Intramedullary nail versus sliding hip screw for stable and unstable trochanteric and subtrochanteric fractures : 17,341 patients from the Norwegian Hip Fracture Register.Bone Joint J. 2022 Feb;104-B(2):274-282. doi: 10.1302/0301-620X.104B2.BJJ-2021-1078.R1. Bone Joint J. 2022. PMID: 35094569
-
A comparison of the long gamma nail with the sliding hip screw for the treatment of AO/OTA 31-A2 fractures of the proximal part of the femur: a prospective randomized trial.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010 Apr;92(4):792-8. doi: 10.2106/JBJS.I.00508. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010. PMID: 20360500 Clinical Trial.
-
Intramedullary nails versus sliding hip screws for AO/OTA 31-A2 trochanteric fractures in adults: A meta-analysis.Int J Surg. 2017 Jul;43:67-74. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsu.2017.05.042. Epub 2017 May 23. Int J Surg. 2017. PMID: 28549994 Review.
-
Sliding hip screw vs intramedullary nail for AO/OTA31A1-A3: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Injury. 2022 Mar;53(3):1149-1159. doi: 10.1016/j.injury.2021.12.034. Epub 2022 Jan 6. Injury. 2022. PMID: 35027220
Cited by
-
The Role of Preoperative Computed Tomography on the Quality of Reduction and Outcomes in Intertrochanteric Fracture: A Controlled Trial.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Feb 12;2021:8854292. doi: 10.1155/2021/8854292. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33628822 Free PMC article.
-
YOLOX-SwinT algorithm improves the accuracy of AO/OTA classification of intertrochanteric fractures by orthopedic trauma surgeons.Chin J Traumatol. 2025 Jan;28(1):69-75. doi: 10.1016/j.cjtee.2024.04.002. Epub 2024 Apr 23. Chin J Traumatol. 2025. PMID: 38762418 Free PMC article.
-
Offset nail fixation for intertrochanteric fractures improves reduction and lag screw position.PLoS One. 2022 Nov 16;17(11):e0276903. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0276903. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36383515 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartoníček J, Rammelt S. The history of internal fixation of proximal femur fractures Ernst Pohl-the genius behind. Int Orthop 2014;38:2421–2426. - PubMed
-
- Aminian A, Gao F, Fedoriw WW, Zhang LQ, Kalainov DM, Merk BR. Vertically oriented femoral neck fractures: mechanical analysis of four fixation techniques. J Orthop Trauma 2007;21:544–548. - PubMed
-
- Baitner AC, Maurer SG, Hickey DG, et al. Vertical shear fractures of the femoral neck: a biomechanical study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1999;367:300–305. - PubMed
-
- Barton TM, Gleeson R, Topliss C, Greenwood R, Harries WJ, Chesser TJ. A comparison of the long gamma nail with the sliding hip screw for the treatment of AO/OTA 31-A2 fractures of the proximal part of the femur: a prospective randomized trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2010;92:792–798. - PubMed
-
- Bartonícek J. Pauwels’ classification of femoral neck fractures: correct interpretation of the original. J Orthop Trauma 2001;15:358–360. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

