Type 2 Diabetes Remission and Substantial Body Weight Reduction Achieved with Metformin and a Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor
- PMID: 32175210
- PMCID: PMC7051125
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.7110
Type 2 Diabetes Remission and Substantial Body Weight Reduction Achieved with Metformin and a Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor
Abstract
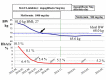
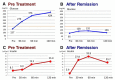
The overall goal in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is remission. However, the effects of a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor (SGLT2i) on remission of T2DM are unknown. We herein report a case involving an overweight 43-year-old man who completely recovered from T2DM after SGLT2i therapy (dapagliflozin at 5 mg/day). In the pretreatment period, he had a body mass index (BMI) of 26.0 kg/m2, hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) concentration of 10.3%, advanced insulin resistance, pancreatic β-cell dysfunction, and fatty liver. Eighteen months after comprehensive therapy, including the administration of an SGLT2i and metformin, his BMI had decreased to 21.3 kg/m2 and his glycemic control was almost normal (HbA1c of 5.3%) despite discontinuation of all hypoglycemic medications. This report is the first to propose the usefulness of the combination therapy of SGLT2i and metformin for achieving normal body weight and remission of newly diagnosed T2DM in a real-world clinical situation.
Keywords: diabetes remission; insulin resistance; sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor; types 2 diabetes; weight reduction.
Copyright © 2020, Sugiyama et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared financial relationships, which are detailed in the next section.
Figures

References
-
- Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49) Turner RC, Cull CA, Frighi V, Holman RR, UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/article-abstract/190204. JAMA. 1999;281:2005–2012. - PubMed
-
- Mann JI, Chisholm A, Galbo H, Richter EA. International Textbook of Diabetes Mellitus. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley Blackwell; 2015. Management of diabetes: diet, exercise and drugs; pp. 577–588.
-
- Bennett PH, Knowler WC. Joslin's Diabetes Mellitus. 14th. Boston: Williams & Wilkins; 2005. Definition, diagnosis, and classification of diabetes mellitus and glucose homeostasis; p. 339.
-
- Quantitative relationship between body weight gain in adulthood and incident type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. Kodama S, Horikawa C, Fujihara K, et al. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/obr.12129. Obes Rev. 2014;15:202–214. - PubMed
-
- Ectopic fat in insulin resistance, dyslipidemia, and cardiometabolic disease. Shulman GI. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMra1011035. N Engl J Med. 2014;371:1131–1141. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
