Inducing Endogenous Cardiac Regeneration: Can Biomaterials Connect the Dots?
- PMID: 32175315
- PMCID: PMC7056668
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00126
Inducing Endogenous Cardiac Regeneration: Can Biomaterials Connect the Dots?
Abstract
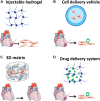
Heart failure (HF) after myocardial infarction (MI) due to blockage of coronary arteries is a major public health issue. MI results in massive loss of cardiac muscle due to ischemia. Unfortunately, the adult mammalian myocardium presents a low regenerative potential, leading to two main responses to injury: fibrotic scar formation and hypertrophic remodeling. To date, complete heart transplantation remains the only clinical option to restore heart function. In the last two decades, tissue engineering has emerged as a promising approach to promote cardiac regeneration. Tissue engineering aims to target processes associated with MI, including cardiomyogenesis, modulation of extracellular matrix (ECM) remodeling, and fibrosis. Tissue engineering dogmas suggest the utilization and combination of two key components: bioactive molecules and biomaterials. This chapter will present current therapeutic applications of biomaterials in cardiac regeneration and the challenges still faced ahead. The following biomaterial-based approaches will be discussed: Nano-carriers for cardiac regeneration-inducing biomolecules; corresponding matrices for their controlled release; injectable hydrogels for cell delivery and cardiac patches. The concept of combining cardiac patches with controlled release matrices will be introduced, presenting a promising strategy to promote endogenous cardiac regeneration.
Keywords: biomaterials; cardiac patch; cardiac regeneration; drug delivery; myocardial infarction; tissue engineering.
Copyright © 2020 Bar and Cohen.
Figures


References
-
- Abdel-Latif A., Bolli R., Zuba-Surma E. K., Tleyjeh I. M., Hornung C. A., Dawn B. (2008). Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor therapy for cardiac repair after acute myocardial infarction: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am. Heart J. 156 216–226.e9. 10.1016/j.ahj.2008.03.024 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Anker S. D., Coats A. J. S., Cristian G., Dragomir D., Pusineri E., Piredda M., et al. (2015). A prospective comparison of alginate-hydrogel with standard medical therapy to determine impact on functional capacity and clinical outcomes in patients with advanced heart failure (AUGMENT-HF trial). Eur. Heart J. 36 2297–2309. 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv259 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

