Resolving the Complexity of Ubiquitin Networks
- PMID: 32175328
- PMCID: PMC7056813
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00021
Resolving the Complexity of Ubiquitin Networks
Abstract
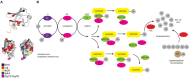
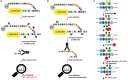
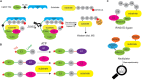
Ubiquitination regulates nearly all cellular processes by coordinated activity of ubiquitin writers (E1, E2, and E3 enzymes), erasers (deubiquitinating enzymes) and readers (proteins that recognize ubiquitinated proteins by their ubiquitin-binding domains). By differentially modifying cellular proteome and by recognizing these ubiquitin modifications, ubiquitination machinery tightly regulates execution of specific cellular events in space and time. Dynamic and complex ubiquitin architecture, ranging from monoubiquitination, multiple monoubiquitination, eight different modes of homotypic and numerous types of heterogeneous polyubiquitin linkages, enables highly dynamic and complex regulation of cellular processes. We discuss available tools and approaches to study ubiquitin networks, including methods for the identification and quantification of ubiquitin-modified substrates, as well as approaches to quantify the length, abundance, linkage type and architecture of different ubiquitin chains. Furthermore, we also summarize the available approaches for the discovery of novel ubiquitin readers and ubiquitin-binding domains, as well as approaches to monitor and visualize activity of ubiquitin conjugation and deconjugation machineries. We also discuss benefits, drawbacks and limitations of available techniques, as well as what is still needed for detailed spatiotemporal dissection of cellular ubiquitination networks.
Keywords: E3 ligase; affinity purification; deubiquitinating enzyme; mass spectrometry; ubiquitin; ubiquitin receptor.
Copyright © 2020 Kliza and Husnjak.
Figures






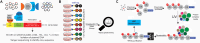
References
-
- Akimov V., Olsen L. C. B., Hansen S. V. F., Barrio-Hernandez I., Puglia M., Jensen S. S., et al. (2018b). StUbEx PLUS-A modified stable tagged ubiquitin exchange system for peptide level purification and in-depth mapping of ubiquitination sites. J. Proteome Res. 17 296–304. 10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00566 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

