Promising Biocompatible, Biodegradable, and Inert Polymers for Purification of Wastewater by Simultaneous Removal of Carcinogenic Cr(VI) and Present Toxic Heavy Metal Cations: Reduction of Chromium(VI) by Poly(ethylene glycol) in Aqueous Perchlorate Solutions
- PMID: 32175490
- PMCID: PMC7066562
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.9b03485
Promising Biocompatible, Biodegradable, and Inert Polymers for Purification of Wastewater by Simultaneous Removal of Carcinogenic Cr(VI) and Present Toxic Heavy Metal Cations: Reduction of Chromium(VI) by Poly(ethylene glycol) in Aqueous Perchlorate Solutions
Abstract
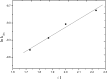
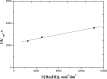
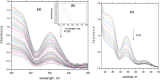
A spectrophotometric technique has been applied for studying the reduction of chromium(VI) by poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) as water-soluble and nontoxic synthetic polymer at a constant ionic strength of 4.0 mol dm-3 in the absence and presence of the ruthenium(III) catalyst. In the absence of the catalyst, the reaction orders in [Cr(VI)] and [PEG] were found to be unity and fractional first orders, respectively. The oxidation process was found to be acid-catalyzed with fractional second order in [H+]. The addition of Ru(III) was found to catalyze the oxidation rates with observation of zero-order reaction in [CrO4 2-] and fractional orders in both [PEG] and [Ru(III)], respectively. The PEG reduces the soluble toxic hexavalent Cr(VI) as a model pollutant to the insoluble nontoxic Cr(III) complex, which is known to be eco-friendly and more safer from the environmental points of view. The acid derivative of PEG was found to possess high affinity for the removal of poisonous heavy metal ions from contaminant matters by chelation. Formation of the 1:1 intermediate complex has been kinetically revealed. A consistent reaction mechanism of oxidation was postulated and discussed.
Copyright © 2020 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




References
-
- Harris J. M.Poly(ethylene Glycol) chemistry, introduction to chemistry and biological applications of poly (ethylene glycol); Plenum Press: New York, 1993.
-
- Royer G. P.; Anantharmaiah G. M. Peptide synthesis in water and the use of immobilized carboxypeptidase Y for deprotection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1979, 101, 3394–3396. 10.1021/ja00506a051. - DOI
-
- Ulbrich K.; Strohalm J.; Kopec̆ek J. Poly(ethylene glycol)s containing enzymatically degradable bonds. Makromol. Chem. 1986, 187, 1131–1144. 10.1002/macp.1986.021870510. - DOI
-
- Ouchi T.; Hagihara Y.; Takahashi K.; Takano Y.; Igarashi I. Synthesis and antitumor activity of poly(ethylene glycol)s linked to 5-fluorouracil via a urethane or urea bond. Drug Des. Discovery 1992, 9, 93–105. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
