An abundant quiescent stem cell population in Drosophila Malpighian tubules protects principal cells from kidney stones
- PMID: 32175841
- PMCID: PMC7093152
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.54096
An abundant quiescent stem cell population in Drosophila Malpighian tubules protects principal cells from kidney stones
Abstract
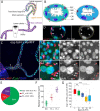
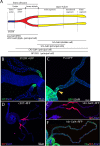
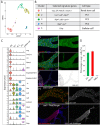
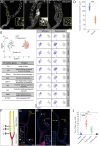
Adult Drosophila Malpighian tubules have low rates of cell turnover but are vulnerable to damage caused by stones, like their mammalian counterparts, kidneys. We show that Drosophilarenal stem cells (RSCs) in the ureter and lower tubules comprise a unique, unipotent regenerative compartment. RSCs respond only to loss of nearby principal cells (PCs), cells critical for maintaining ionic balance. Large polyploid PCs are outnumbered by RSCs, which replace each lost cell with multiple PCs of lower ploidy. Notably, RSCs do not replenish principal cells or stellate cells in the upper tubules. RSCs generate daughters by asymmetric Notch signaling, yet RSCs remain quiescent (cell cycle-arrested) without damage. Nevertheless, the capacity for RSC-mediated repair extends the lifespan of flies carrying kidney stones. We propose that abundant, RSC-like stem cells exist in other tissues with low rates of turnover where they may have been mistaken for differentiated tissue cells.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; Drosophila; developmental biology; kidney; kidney stone; malphigian tubule; quiescent; stem cell.
© 2020, Wang and Spradling.
Conflict of interest statement
CW, AS No competing interests declared
Figures


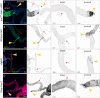
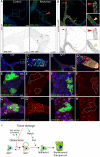
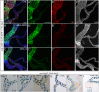

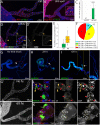


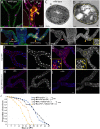
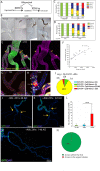
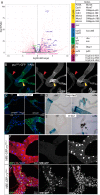
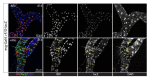
References
-
- Angelotti ML, Ronconi E, Ballerini L, Peired A, Mazzinghi B, Sagrinati C, Parente E, Gacci M, Carini M, Rotondi M, Fogo AB, Lazzeri E, Lasagni L, Romagnani P. Characterization of renal progenitors committed toward tubular lineage and their regenerative potential in renal tubular injury. Stem Cells. 2012;30:1714–1725. doi: 10.1002/stem.1130. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

