A novel EDA1 missense mutation in X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
- PMID: 32176048
- PMCID: PMC7220389
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000019244
A novel EDA1 missense mutation in X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia
Abstract
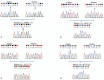
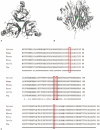
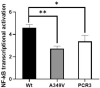
A mutation in the epithelial morphogen gene ectodysplasin-A1 (EDA1) is responsible for the disorder X-linked hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia (XLHED), the most common form of ectodermal dysplasia. XLHED is characterized by impaired development of hair, eccrine sweat glands, and teeth. This study aimed to identify potentially pathogenic mutations in four Chinese XLHED families.Genomic DNA was extracted from the peripheral blood and sequenced. Sanger sequencing was used to carry out mutational analysis of the EDA1 gene, and the three-dimensional structure of the novel mutant residues in the EDA trimer was determined. Transcriptional activity of NF-κB was tested by Dual luciferin assay.We identified a novel EDA1 mutation (c.1046C>T) and detected 3 other previously-reported mutations (c.146T>A; c.457C>T; c.467G>A). Our findings demonstrated that novel mutation c.1046C>T (p.A349 V) resulted in XLHED. The novel mutation could cause volume repulsion in the protein due to enlargement of the amino acid side chain. Dual luciferase assay revealed that transcriptional NF-κB activation induced by XLHED EDA1 protein was significantly reduced compared with wild-type EDA1.These results extend the spectrum of EDA1 mutations in XLHED patients and suggest a functional role of the novel mutation in XLHED.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures

References
-
- Mikkola ML. Molecular aspects of hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia. Am J Med Genet A 2009;149A:2031–6. - PubMed
-
- Kere J, Srivastava AK, Montonen O, et al. X-linked anhidrotic (hypohidrotic) ectodermal dysplasia is caused by mutation in a novel transmembrane protein. Nat Genet 1996;13:409–16. - PubMed
-
- Visinoni AF, Lisboa-Costa T, Pagnan NA, et al. Ectodermal dysplasias: clinical and molecular review. Am J Med Genet A 2009;149A:1980–2002. - PubMed
-
- Laurikkala J, Mikkola M, Mustonen T, et al. TNF signaling via the ligand–receptor pair ectodysplasin and edar controls the function of epithelial signaling centers and is regulated by Wnt and activin during tooth organogenesis. Dev Biol 2001;229:443–55. - PubMed
-
- Itin PH, Fistarol SK. Ectodermal dysplasias. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 2004;131C:45–51. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

