Implementing a Learning Collaborative Framework for States Working to Improve Outcomes for Vulnerable Populations: The Opioid Use Disorder, Maternal Outcomes, and Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Initiative Learning Community
- PMID: 32176568
- PMCID: PMC7259818
- DOI: 10.1089/jwh.2020.8303
Implementing a Learning Collaborative Framework for States Working to Improve Outcomes for Vulnerable Populations: The Opioid Use Disorder, Maternal Outcomes, and Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Initiative Learning Community
Abstract
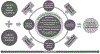
The opioid crisis has impacted vulnerable populations, specifically pregnant and postpartum women, and infants prenatally exposed to substances, including infants with Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome. Lack of access to clinical and social services; potential stigma or discrimination; and lack of resources for provision of services, including screening and treatment, have impacted the health of these populations. In 2018, using a systems change approach, the Association of State and Territorial Health Officials (ASTHO) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) convened an Opioid use disorder, Maternal outcomes, Neonatal abstinence syndrome Initiative Learning Community (OMNI LC) that included other federal agencies, national clinical and nonclinical organizations, and 12 state leadership groups. The purpose of the OMNI LC was to determine areas of focus and identify strategies and best practices for implementing systems change to improve maternal and infant outcomes associated with opioid use disorder (OUD) during the perinatal period. Activities included in-person convenings with policy goal action plan development, virtual learning sessions, intensive technical assistance (TA), and temporary field placements. The OMNI LC partnering agencies and state teams met bimonthly for the first year of the initiative. At the in-person convening, state teams identified barriers to developing and implementing systems change in activity-specific action plans within five areas of focus: financing and coverage; access to and coordination of quality services; provider training and awareness; ethical, legal, and social considerations; and data, monitoring, and evaluation. State teams also identified stakeholder partnerships as a necessary component of strategy development in all areas of focus. Four virtual learning sessions were conducted on the areas of focus identified by state teams, and ASTHO conducted three intensive TA opportunities, and five states were identified for temporary field placement. To successfully address the impact of the opioid crisis on pregnant and postpartum women and infants, states developed innovative strategies focused on increasing support, services, and resources. Moving forward, state teams will participate in two additional in-person meetings, continue to identify barriers to the work, refine and customize action plans, and set new goals, to effect broad-ranging systems change for these vulnerable populations.
Keywords: learning collaboratives; neonatal abstinence syndrome; opioid addiction; opioid crisis; opioid use disorder; postpartum; pregnancy.
Figures

References
-
- Gostin LO, Hodge JG Jr., Noe SA. Reframing the opioid epidemic as a national emergency. JAMA 2017;318:1539–1540. - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association: Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th ed. Arlington, VA: American Psychiatric Publishing, 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

