Trends in the Recent Patent Literature on Cholinesterase Reactivators (2016-2019)
- PMID: 32178264
- PMCID: PMC7175240
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10030436
Trends in the Recent Patent Literature on Cholinesterase Reactivators (2016-2019)
Abstract
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) is the key enzyme responsible for deactivating the ACh neurotransmitter. Irreversible or prolonged inhibition of AChE, therefore, elevates synaptic ACh leading to serious central and peripheral adverse effects which fall under the cholinergic syndrome spectra. To combat the toxic effects of some AChEI, such as organophosphorus (OP) nerve agents, many compounds with reactivator effects have been developed. Within the most outstanding reactivators, the substances denominated oximes stand out, showing good performance for reactivating AChE and restoring the normal synaptic acetylcholine (ACh) levels. This review was developed with the purpose of covering the new advances in AChE reactivation. Over the past years, researchers worldwide have made efforts to identify and develop novel active molecules. These researches have been moving farther into the search for novel agents that possess better effectiveness of reactivation and broad-spectrum reactivation against diverse OP agents. In addition, the discovery of ways to restore AChE in the aged form is also of great importance. This review will allow us to evaluate the major advances made in the discovery of new acetylcholinesterase reactivators by reviewing all patents published between 2016 and 2019. This is an important step in continuing this remarkable research so that new studies can begin.
Keywords: acetylcholinesterase; new trends in reactivators; organophosphorus compounds; reactivation process; therapeutic potential.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




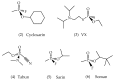

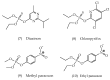


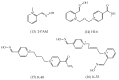


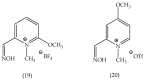



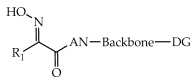

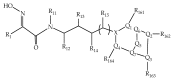

References
-
- Kassa J., Korabecny J., Nepovimova E., Jun D. The influence of modulators of acetylcholinesterase on the resistance of mice against soman and on the effectiveness of antidotal treatment of soman poisoning in mice. J. Appl. Biomed. 2018;16:10–14. doi: 10.1016/j.jab.2017.01.004. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

