Tannic Acid Improves Renal Function Recovery after Renal Warm Ischemia-Reperfusion in a Rat Model
- PMID: 32178273
- PMCID: PMC7175177
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10030439
Tannic Acid Improves Renal Function Recovery after Renal Warm Ischemia-Reperfusion in a Rat Model
Abstract
Background and purpose: Ischemia-reperfusion injury is encountered in numerous processes such as cardiovascular diseases or kidney transplantation; however, the latter involves cold ischemia, different from the warm ischemia found in vascular surgery by arterial clamping. The nature and the intensity of the processes induced by ischemia types are different, hence the therapeutic strategy should be adapted. Herein, we investigated the protective role of tannic acid, a natural polyphenol in a rat model reproducing both renal warm ischemia and kidney allotransplantation. The follow-up was done after 1 week.
Experimental approach: To characterize the effect of tannic acid, an in vitro model of endothelial cells subjected to hypoxia-reoxygenation was used.
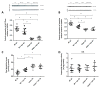
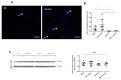
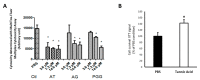
Key results: Tannic acid statistically improved recovery after warm ischemia but not after cold ischemia. In kidneys biopsies, 3h after warm ischemia-reperfusion, oxidative stress development was limited by tannic acid and the production of reactive oxygen species was inhibited, potentially through Nuclear Factor erythroid-2-Related factor 2 (NRF2) activation. In vitro, tannic acid and its derivatives limited cytotoxicity and the generation of reactive oxygen species. Molecular dynamics simulations showed that tannic acid efficiently interacts with biological membranes, allowing efficient lipid oxidation inhibition. Tannic acid also promoted endothelial cell migration and proliferation during hypoxia.
Conclusions: Tannic acid was able to improve renal recovery after renal warm ischemia with an antioxidant effect putatively extended by the production of its derivatives in the body and promoted cell regeneration during hypoxia. This suggests that the mechanisms induced by warm and cold ischemia are different and require specific therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: cold ischemia; oxidative stress; renal function recovery; tannic acid; warm ischemia.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to disclose by any of the authors.
Figures











References
-
- Khalifeh T., Baulier E., Le Pape S., Kerforne T., Coudroy R., Maiga S., Hauet T., Pinsard M., Favreau F. Strategies to optimize kidney recovery and preservation in transplantation: Specific aspects in pediatric transplantation. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2014;30:1243–1254. doi: 10.1007/s00467-014-2924-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Do G.M., Kwon E.Y., Ha T.Y., Park Y.B., Kim H.J., Jeon S.M., Lee M.K., Choi M.S. Tannic acid is more effective than clofibrate for the elevation of hepatic beta-oxidation and the inhibition of 3-hydroxy-3-methyl-glutaryl-CoA reductase and aortic lesion formation in apo E-deficient mice. Br. J. Nutr. 2011;106:1855–1863. doi: 10.1017/S000711451100256X. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Lopes G.K., Schulman H.M., Hermes-Lima M. Polyphenol tannic acid inhibits hydroxyl radical formation from Fenton reaction by complexing ferrous ions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1999:1472. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

