Network Pharmacology-Based Approaches of Rheum undulatum Linne and Glycyrriza uralensis Fischer Imply their Regulation of Liver Failure with Hepatic Encephalopathy in Mice
- PMID: 32178308
- PMCID: PMC7175377
- DOI: 10.3390/biom10030437
Network Pharmacology-Based Approaches of Rheum undulatum Linne and Glycyrriza uralensis Fischer Imply their Regulation of Liver Failure with Hepatic Encephalopathy in Mice
Abstract
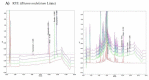
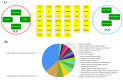
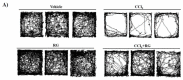
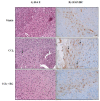
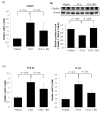
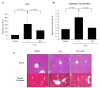
Rheum undulatum and Glycyrrhiza uralensis have been used as supplementary ingredients in various herbal medicines. They have been reported to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects and, therefore, have potential in the treatment and prevention of various liver diseases. Considering that hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is often associated with chronic liver failure, we investigated whether an R. undulatum and G. uralensis extract mixture (RG) could reduce HE. We applied systems-based pharmacological tools to identify the active ingredients in RG and the pharmacological targets of RG by examining mechanism-of-action profiles. A CCl4-induced HE mouse model was used to investigate the therapeutic mechanisms of RG on HE. We successfully identified seven bioactive ingredients in RG with 40 potential targets. Based on an integrated target-disease network, RG was predicted to be effective in treating neurological diseases. In animal models, RG consistently relieved HE symptoms by protecting blood-brain barrier permeability via downregulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and upregulation of claudin-5. In addition, RG inhibited mRNA expression levels of both interleukin (IL)-1β and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1. Based on our results, RG is expected to function various biochemical processes involving neuroinflammation, suggesting that RG may be considered a therapeutic agent for treating not only chronic liver disease but also HE.
Keywords: Glycyrriza uralensis; MMP-9; Rheum undulatum; hepatic encephalopathy; neuroinflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Vilstrup H., Amodio P., Bajaj J., Cordoba J., Ferenci P., Mullen K.D., Weissenborn K., Wong P. Hepatic encephalopathy in chronic liver disease: 2014 Practice Guideline by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases and the European Association for the Study of the Liver. Hepatology. 2014;60:715–735. doi: 10.1002/hep.27210. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dadsetan S., Waagepetersen H.S., Schousboe A., Bak L.K. Glutamine and ammonia in hepatic encephalopathy. In: Rajendram R., Preedy V.R., Patel V.B., editors. Glutamine in Clinical Nutrition. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2015.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

