The Roles of miRNA in Glioblastoma Tumor Cell Communication: Diplomatic and Aggressive Negotiations
- PMID: 32178454
- PMCID: PMC7139390
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21061950
The Roles of miRNA in Glioblastoma Tumor Cell Communication: Diplomatic and Aggressive Negotiations
Abstract
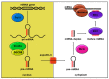
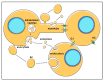
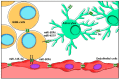
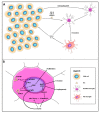
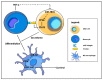
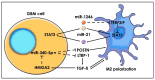
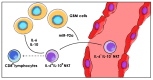
Glioblastoma (GBM) consists of a heterogeneous collection of competing cellular clones which communicate with each other and with the tumor microenvironment (TME). MicroRNAs (miRNAs) present various exchange mechanisms: free miRNA, extracellular vesicles (EVs), or gap junctions (GJs). GBM cells transfer miR-4519 and miR-5096 to astrocytes through GJs. Oligodendrocytes located in the invasion front present high levels of miR-219-5p, miR-219-2-3p, and miR-338-3p, all related to their differentiation. There is a reciprocal exchange between GBM cells and endothelial cells (ECs) as miR-5096 promotes angiogenesis after being transferred into ECs, whereas miR-145-5p acts as a tumor suppressor. In glioma stem cells (GSCs), miR-1587 and miR-3620-5p increase the proliferation and miR-1587 inhibits the hormone receptor co-repressor-1 (NCOR1) after EVs transfers. GBM-derived EVs carry miR-21 and miR-451 that are up-taken by microglia and monocytes/macrophages, promoting their proliferation. Macrophages release EVs enriched in miR-21 that are transferred to glioma cells. This bidirectional miR-21 exchange increases STAT3 activity in GBM cells and macrophages, promoting invasion, proliferation, angiogenesis, and resistance to treatment. miR-1238 is upregulated in resistant GBM clones and their EVs, conferring resistance to adjacent cells via the CAV1/EGFR signaling pathway. Decrypting these mechanisms could lead to a better patient stratification and the development of novel target therapies.
Keywords: glioblastoma; intercellular communication; miRNA; tumor microenvironment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of miR-9-5p, miR-124-3p, miR-21-5p, miR-138-5p, and miR-1-3p in Glioblastoma Cell Lines and Extracellular Vesicles.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 11;21(22):8491. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228491. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33187334 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-338-5p sensitizes glioblastoma cells to radiation through regulation of genes involved in DNA damage response.Tumour Biol. 2016 Jun;37(6):7719-27. doi: 10.1007/s13277-015-4654-x. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Tumour Biol. 2016. PMID: 26692101
-
Inhibition of tumor progression and M2 microglial polarization by extracellular vesicle-mediated microRNA-124 in a 3D microfluidic glioblastoma microenvironment.Theranostics. 2021 Sep 27;11(19):9687-9704. doi: 10.7150/thno.60851. eCollection 2021. Theranostics. 2021. PMID: 34646393 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Glioblastoma Tumor Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2020 Jan 21;10:3137. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.03137. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32038644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA and extracellular vesicles in glioblastoma: small but powerful.Brain Tumor Pathol. 2016 Apr;33(2):77-88. doi: 10.1007/s10014-016-0259-3. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2016. PMID: 26968172 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Circulating hsa-miR-5096 predicts 18F-FDG PET/CT positivity and modulates somatostatin receptor 2 expression: a novel miR-based assay for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.Front Oncol. 2023 May 23;13:1136331. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1136331. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37287922 Free PMC article.
-
Agathisflavone Inhibits Viability and Modulates the Expression of miR-125b, miR-155, IL-6, and Arginase in Glioblastoma Cells and Microglia/Macrophage Activation.Molecules. 2025 Jan 3;30(1):158. doi: 10.3390/molecules30010158. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 39795214 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of circular JUN prevents the proliferation and invasion of glioblastoma via miR-3064-IGFBP5 axis.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Sep;28(18):e70098. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70098. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39307884 Free PMC article.
-
The Biological Processes of Ferroptosis Involved in Pathogenesis of COVID-19 and Core Ferroptoic Genes Related With the Occurrence and Severity of This Disease.Evol Bioinform Online. 2023 Feb 13;19:11769343231153293. doi: 10.1177/11769343231153293. eCollection 2023. Evol Bioinform Online. 2023. PMID: 36820229 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of MicroRNAs in Therapeutic Resistance of Malignant Primary Brain Tumors.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 7;9:740303. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.740303. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34692698 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Louis D.N., Perry A., Reifenberger G., von Deimling A., Figarella-Branger D., Cavenee W.K., Ohgaki H., Wiestler O.D., Kleihues P., Ellison D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:803–820. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ostrom Q.T., Gittleman H., Farah P., Ondracek A., Chen Y., Wolinsky Y., Stroup N.E., Kruchko C., Barnholtz-Sloan J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2006-2010. Neuro-Oncology. 2013;15:ii1–ii56. doi: 10.1093/neuonc/not151. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Smith J.S., Tachibana I., Passe S.M., Huntley B.K., Borell T.J., Iturria N., O’Fallon J.R., Schaefer P.L., Scheithauer B.W., James C.D., et al. PTEN Mutation, EGFR Amplification, and Outcome in Patients With Anaplastic Astrocytoma and Glioblastoma Multiforme. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2001;93:1246–1256. doi: 10.1093/jnci/93.16.1246. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

