Is insurance instability associated with hypertension outcomes and does this vary by race/ethnicity?
- PMID: 32178663
- PMCID: PMC7077125
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-020-05095-8
Is insurance instability associated with hypertension outcomes and does this vary by race/ethnicity?
Abstract
Background: Stable health insurance is often associated with better chronic disease care and outcomes. Racial/ethnic health disparities in outcomes are prevalent and may be associated with insurance instability, particularly in the context of health insurance reform.
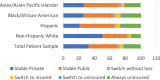
Methods: We examined whether insurance instability was associated with uncontrolled blood pressure (UBP) and whether this association varied by race/ethnicity. We used a retrospective longitudinal observational cohort study of patients diagnosed with hypertension who obtained care within two health systems in Massachusetts. We measured the UBP, insurance instability, and race of 43,785 adult primary care patients, age 21-64 with visits from 1/2005-12/2013.
Results: We found higher rates of UBP for blacks and Hispanics at each time point over the entire 9 years. Insurance instability was associated with greater rates of UBP. Always uninsured black patients fared worst, while white and Hispanic patients with consistent public insurance fared best.
Conclusions: Stable insurance of any type was associated with better hypertension control than no or unstable insurance.
Keywords: Health; Health status disparity; Hypertension; Insurance.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sommers BD, Gawande AA, Baicker K. Health insurance coverage and health - what the recent evidence tells us. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(6):586–93. - PubMed
-
- Wilper AP, Woolhandler S, Lasser KE, McCormick D, Bor DH, Himmelstein DU. Hypertension, diabetes, and elevated cholesterol among insured and uninsured U.S. adults. Health Affairs (Project Hope). 2009;28(6):w1151–9. - PubMed
-
- McWilliams JM, Meara E, Zaslavsky AM, Ayanian JZ. Differences in control of cardiovascular disease and diabetes by race, ethnicity, and education: U.S. trends from 1999 to 2006 and effects of medicare coverage. Ann Intern Med. 2009;150(8):505–515. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-150-8-200904210-00005. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical