Efficacy of Tuina in patients with chronic low back pain: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
- PMID: 32178704
- PMCID: PMC7077020
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-020-4198-2
Efficacy of Tuina in patients with chronic low back pain: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Low back pain is a common reason for medical care and carries a heavy social burden. The efficacy of Tuina or health care education for low back pain has been evaluated in previous systematic reviews. However, there is no evidence to support the superiority of one form of treatment over another. The aim of this study is to compare the efficacy of Tuina with health care education in the management of low back pain.
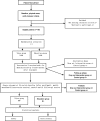
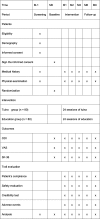
Methods/design: This study is a randomized controlled trial with parallel-group design including two groups: a Tuina group and a health care education group. A total of 160 eligible participants will be randomly assigned to the groups in a 1:1 ratio. The interventions of both groups will last for 20 min and be carried out twice each week for a period of 12 weeks. The primary outcome is the Oswestry Disability Index. The secondary outcomes include a visual analogue scale and the 36-item Short Form Health Survey. They will be assessed at baseline, at the end of the intervention every month, and during 6 months and 9 months of follow-up by repeated measures analysis of variance. The significance level is 5%. The safety of Tuina and health care education will be evaluated after each treatment session. This study will focus on the value of Tuina and health care education for low back pain and will highlight any differences in the efficacy of the treatments.
Discussion: This study will evaluate the efficacy and safety of Tuina intervention for low back pain, which could provide reliable evidence for clinical decision making for patients with low back pain.
Trial registration: Chinese Clinical Trial Registry, ChiCTR1900022656. Registered on 23 April 2019.
Keywords: Efficacy; Health care education; Low back pain; Randomized controlled trial; Tuina.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- 16CR1023A/Shenkang Three-Year Action Plan "Clinical Skills Enhancement Project for Major Diseases"
- ZY(2018-2020)-FWTX-2005/National Key Clinical Difficult Diseases Clinical Collaborative Pilot Construction Project - Osteoarticular Degenerative Disease
- ZY (2018-2020)-CCCX-2004-02/Shanghai Further accelerate the three-year action plan for the development of Chinese medicine
- 2018LP040/Shanghai Health and Family Planning Commission Chinese Medicine Research Project
- 2018YQ004/Shanghai Health and Family Planning System Outstanding Young Medical Talents
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

