RNA interference screening methods to identify proliferation determinants and mechanisms of resistance to immune attack
- PMID: 32178823
- PMCID: PMC7533725
- DOI: 10.1016/bs.mie.2019.06.002
RNA interference screening methods to identify proliferation determinants and mechanisms of resistance to immune attack
Abstract
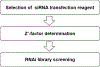
We have used RNA interference (RNAi) screening technology to reveal unknown components of biological signaling pathways including survival mechanisms of estrogen-independent breast cancer cell growth and cancer cell resistance to immune attack. In this chapter, a detailed protocol describing the use of RNAi screening to identify factors important for the proliferation of estrogen-independent MCF7 breast cancer cells will be described. Resistance to therapies that target the estrogen pathway remains a challenge in the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. To address this challenge, small interfering-RNA (siRNA)-based libraries targeting an estrogen receptor (ER)- and aromatase-centered network, including 631 genes relevant to estrogen signaling, was designed and constructed for RNAi screening. This protocol will include the following parts: (1) selection of RNAi transfection reagent for specific cells; (2) optimization of RNAi screening conditions using Z'-factor; (3) procedure of ER-network gene siRNA library screening using automated machines under optimized experimental conditions; and (4) method of analysis for RNAi screening data to identify specific determinants important for cell proliferation. 46 genes were found to be selectively required for the survival of estrogen-independent MCF7-derived cells.
Keywords: Breast cancer; CyBio automatic dispenser; Estrogen receptor (ER); Immunotherapy; Multidrop Combi-nL reagent dispenser; RNA interference (RNAi); Screening; WellMate microplate dispenser; Z′-factor.
© 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

