Hindbrain melanocortin 3/4 receptors modulate the food intake and body weight suppressive effects of the GLP-1 receptor agonist, liraglutide
- PMID: 32179053
- PMCID: PMC7227776
- DOI: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2020.112870
Hindbrain melanocortin 3/4 receptors modulate the food intake and body weight suppressive effects of the GLP-1 receptor agonist, liraglutide
Abstract
Simultaneously targeting multiple energy balance control systems is a promising direction for the development of obesity pharmacotherapies. Here, we explore the interaction between the GLP-1 and melanocortin system within the dorsal vagal complex (DVC) of the caudal brainstem. Using a pharmacological approach, we demonstrate that the full anorectic potential of liraglutide, an FDA-approved GLP-1 analog for the treatment of obesity, requires DVC melanocortin 3/4 receptor (MC3/4R) signaling. Specifically, the food intake and body weight suppressive effects of liraglutide were attenuated by DVC administration of the MC3/4R antagonist SHU9119. In contrast, the anorectic effects of liraglutide were enhanced by combined activation of DVC MC3/4Rs using the agonist MTII. Our findings highlight the modulation of liraglutide-induced anorexia by DVC MC3/4R signaling, thereby suggesting a site of action at which two important energy balance control systems interact.
Keywords: Area postrema; Brainstem; MSH; NTS; Obesity; POMC.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest MRH also receives research funding from Zealand Pharma, Eli Lilly & Co., Novo Nordisk and Boehringer Ingelheim that was not used in support of these studies. All other authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
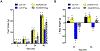
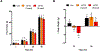

References
-
- Hales CM, Carroll MD, Fryar CD, Ogden CL, Prevalence of Obesity Among Adults and Youth: United States, 2015–2016 Key findings Data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2015.
-
- Jeffery RW, Drewnowski A, Epstein LH, Stunkard AJ, Wilson GT, Wing RR, Hill DR, Long-term maintenance of weight loss: current status., Health Psychol. 19 (2000) 5–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

