Significant Efficacy of a Single Low Dose of Primaquine Compared to Stand-Alone Artemisinin Combination Therapy in Reducing Gametocyte Carriage in Cambodian Patients with Uncomplicated Multidrug-Resistant Plasmodium falciparum Malaria
- PMID: 32179526
- PMCID: PMC7269483
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.02108-19
Significant Efficacy of a Single Low Dose of Primaquine Compared to Stand-Alone Artemisinin Combination Therapy in Reducing Gametocyte Carriage in Cambodian Patients with Uncomplicated Multidrug-Resistant Plasmodium falciparum Malaria
Abstract
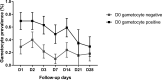
Since 2012, a single low dose of primaquine (SLDPQ; 0.25 mg/kg of body weight) with artemisinin-based combination therapies has been recommended as the first-line treatment of acute uncomplicated Plasmodium falciparum malaria to interrupt its transmission, especially in low-transmission settings of multidrug resistance, including artemisinin resistance. Policy makers in Cambodia have been reluctant to implement this recommendation due to primaquine safety concerns and a lack of data on its efficacy. In this randomized controlled trial, 109 Cambodians with acute uncomplicated P. falciparum malaria received dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine (DP) alone or combined with SLDPQ on the first treatment day. The transmission-blocking efficacy of SLDPQ was evaluated on days 0, 1, 2, 3, 7, 14, 21, and 28, and recrudescence by reverse transcriptase PCR (RT-PCR) (gametocyte prevalence) and membrane feeding assays with Anopheles minimus mosquitoes (gametocyte infectivity). Without the influence of recrudescent infections, DP-SLDPQ reduced gametocyte carriage 3-fold compared to that achieved with DP. Of 48 patients tested on day 0, only 3 patients were infectious to mosquitoes (∼6%). Posttreatment, three patients were infectious on day 14 (3.5%, 1/29) and on the 1st and 7th days of recrudescence (8.3%, 1/12 for each); this overall low infectivity precluded our ability to assess its transmission-blocking efficacy. Our study confirms the effective gametocyte clearance of SLDPQ when combined with DP in multidrug-resistant P. falciparum infections and the negative impact of recrudescent infections due to poor DP efficacy. Artesunate-mefloquine (ASMQ) has replaced DP, and ASMQ-SLDPQ has been deployed to treat all patients with symptomatic P. falciparum infections to further support the elimination of multidrug-resistant P. falciparum in Cambodia. (This study has been registered at ClinicalTrials.gov under identifier NCT02434952.).
Keywords: direct membrane feeding assays; malaria; primaquine; transmission blocking.
Copyright © 2020 Vantaux et al.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. 2019. World malaria report 2019. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland.
-
- Dondorp AM, Nosten F, Yi P, Das D, Phyo AP, Tarning J, Lwin KM, Ariey F, Hanpithakpong W, Lee SJ, Ringwald P, Silamut K, Imwong M, Chotivanich K, Lim P, Herdman T, An SS, Yeung S, Singhasivanon P, Day NPJ, Lindegardh N, Socheat D, White NJ. 2009. Artemisinin resistance in Plasmodium falciparum malaria. N Engl J Med 361:455–467. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0808859. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saunders DL, Vanachayangkul P, Lon C, U.S. Army Military Malaria Research Program, National Center for Parasitology, Entomology, and Malaria Control (CNM), Royal Cambodian Armed Forces . 2014. Dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine failure in Cambodia. N Engl J Med 371:484–485. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1403007. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Leang R, Taylor WR, Bouth DM, Song L, Tarning J, Char MC, Kim S, Witkowski B, Duru V, Domergue A, Khim N, Ringwald P, Menard D. 2015. Evidence of Plasmodium falciparum malaria multidrug resistance to artemisinin and piperaquine in western Cambodia: dihydroartemisinin-piperaquine open-label multicenter clinical assessment. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 59:4719–4726. doi: 10.1128/AAC.00835-15. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

