Grape seed extract: having a potential health benefits
- PMID: 32180617
- PMCID: PMC7054588
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-019-04113-w
Grape seed extract: having a potential health benefits
Abstract
Grapes are one of the most highly consumed fruits across the world. In ancient Europe the leaves and the sap of grape plants has been used in traditional treatment for ages. Besides being a wellspring for vitamins and fibre, the skin and seeds of grapes are highly rich in Polyphenols specifically proanthocyanidins, which can be used as a functional ingredient to address various health issues by boosting the natural bio-processes of the body. Since, grape seeds are by product of wine making companies therefore can be easily procured. The present review article briefly describes the various pharmacological activities of grape seed extract and different experimental studies were done which supports the beneficial health qualities of the extract. Through different and various studies, it was proved that the proanthocyanidin rich grape seed extract provides benefits against many diseases i.e. inflammation, cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes, cancer, peptic ulcer, microbial infections, etc. Therefore, beside from using it as a nutraceutical or cosmeceutical, as a result they may have a potential to substitute or complement in currently used drugs in the treatment of diseases by developing it into other successful pharmaceutical formulations for better future prospective.
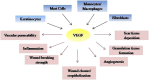
Keywords: Antioxidant; Grape seed extract (GSE); Oxidative stress; Proanthocyanidin; Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF).
© Association of Food Scientists & Technologists (India) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bagchi M, Milnes M, Williams C, et al. Acute and chronic stress-induced oxidative gastrointestinal injury in rats, and the protective ability of a novel grape seed proanthocyanidin extract. Nutr Res. 1999;19(8):1189–1199. doi: 10.1016/S0271-5317(99)00080-9. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
