Prospective Randomized Study Comparing the External Fixator and Volar Locking Plate in Intraarticular Distal Radius Fractures: Which Is Better?
- PMID: 32181084
- PMCID: PMC7053667
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.6849
Prospective Randomized Study Comparing the External Fixator and Volar Locking Plate in Intraarticular Distal Radius Fractures: Which Is Better?
Abstract
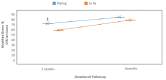
Introduction Various treatment options for patients with an intraarticular distal radius fracture are available, but in cases of comminuted fractures, these narrow down to either a volar locking plate, an external fixator, or a combination of these two. We conducted this prospective study to compare the external fixation and internal fixation of intraarticular fractures of the distal radius in terms of clinical/functional outcome and complications and with the available literature. Material and method This prospective randomized study consisted of a total number of 30 patients with intraarticular fractures of the distal end of the radius divided randomly into two groups (A and B), treated by external fixation (Group A) and volar plating (Group B), in a tertiary care institute during the study period. Result The most patients were males >50 years of age, with injury to the right dominant hand most commonly caused by a fall on an outstretched hand. As per the modified Green & O'Brien scoring system, the volar plating group showed the final result as excellent in two (13.33%), good in seven (46.6%), fair in four (26.6%), and poor in two (13.3%) whereas an excellent outcome was seen in one (6.66%), good and fair in five patients each (33.3%), and poor in four (26.66%) patients at the six months follow-up. Conclusion Overall, both fixation techniques seem to apply sufficient stabilization to restore function and retain anatomy; however, volar locking plates have certain advantages over external fixator in the early postop period in terms of earlier recovery and mobilization.
Keywords: external fixator; intraarticular fracture distal radius; modified green & o’brien score; volar plating.
Copyright © 2020, Sharma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Risk factors for fractures of the distal forearm: a population-based case-control study. Mallmin H, Ljunghall S, Persson I, Bergström R. Osteoporos Int. 1994;4:298–304. - PubMed
-
- Bucholz M, Robert W, Heckman M, Court-Brown CM, Tornetta P. Wolters Kluwer. Pennsylvania, United States: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; 2015. Rockwood and Green’s Fractures in Adults.
-
- A surgical protocol for combined internal and external fixation of complex intraarticular distal radius fractures using dorsal and volar approaches. Jebson PJ, Blair WF. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2378127/ Iowa Orthop J. 1996;16:35–38. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
