Regulation of Autophagy in Cells Infected With Oncogenic Human Viruses and Its Impact on Cancer Development
- PMID: 32181249
- PMCID: PMC7059124
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00047
Regulation of Autophagy in Cells Infected With Oncogenic Human Viruses and Its Impact on Cancer Development
Abstract
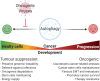
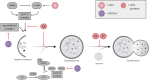
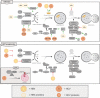
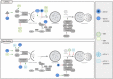
About 20% of total cancer cases are associated to infections. To date, seven human viruses have been directly linked to cancer development: high-risk human papillomaviruses (hrHPVs), Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV), hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV), and human T-lymphotropic virus 1 (HTLV-1). These viruses impact on several molecular mechanisms in the host cells, often resulting in chronic inflammation, uncontrolled proliferation, and cell death inhibition, and mechanisms, which favor viral life cycle but may indirectly promote tumorigenesis. Recently, the ability of oncogenic viruses to alter autophagy, a catabolic process activated during the innate immune response to infections, is emerging as a key event for the onset of human cancers. Here, we summarize the current understanding of the molecular mechanisms by which human oncogenic viruses regulate autophagy and how this negative regulation impacts on cancer development. Finally, we highlight novel autophagy-related candidates for the treatment of virus-related cancers.
Keywords: Epstein–Barr virus (EBV); Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV); Merkel cell polyomavirus (MCPyV); autopaghy; hepatitis B and C viruses (HBV and HCV); human T-lymphotropic virus 1 (HTLV–1); human papillomavirus (HPV); oncogenic (or carcinogenic) viruses.
Copyright © 2020 Vescovo, Pagni, Piacentini, Fimia and Antonioli.
Figures

References
-
- Abe M., Koga H., Yoshida T., Masuda H., Iwamoto H., Sakata M., et al. (2012). Hepatitis C virus core protein upregulates the expression of vascular endothelial growth factor via the nuclear factor-κB/hypoxia-inducible factor-1α axis under hypoxic conditions. Hepatol. Res. 42 591–600. 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2011.00953.x - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

