Glioma stem-like cells evade interferon suppression through MBD3/NuRD complex-mediated STAT1 downregulation
- PMID: 32181805
- PMCID: PMC7201922
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20191340
Glioma stem-like cells evade interferon suppression through MBD3/NuRD complex-mediated STAT1 downregulation
Abstract
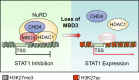
Type I interferons (IFNs) are known to mediate antineoplastic effects during tumor progression. Type I IFNs can be produced by multiple cell types in the tumor microenvironment; however, the molecular mechanisms by which tumor cells evade the inhibition of immune microenvironment remain unknown. Here we demonstrate that glioma stem-like cells (GSCs) evade type I IFN suppression through downregulation of STAT1 to initiate tumor growth under inhospitable conditions. The downregulation of STAT1 is mediated by MBD3, an epigenetic regulator. MBD3 is preferentially expressed in GSCs and recruits NuRD complex to STAT1 promoter to suppress STAT1 expression by histone deacetylation. Importantly, STAT1 overexpression or MBD3 depletion induces p21 transcription, resensitizes GSCs to IFN suppression, attenuates GSC tumor growth, and prolongs animal survival. Our findings demonstrate that inactivation of STAT1 signaling by MBD3/NuRD provides GSCs with a survival advantage to escape type I IFN suppression, suggesting that targeting MBD3 may represent a promising therapeutic opportunity to compromise GSC tumorigenic potential.
© 2020 Zhan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: The authors declare no competing interests exist.
Figures




Similar articles
-
c-Jun N-terminal phosphorylation antagonises recruitment of the Mbd3/NuRD repressor complex.Nature. 2011 Jan 13;469(7329):231-5. doi: 10.1038/nature09607. Epub 2011 Jan 2. Nature. 2011. PMID: 21196933
-
The proto-oncoprotein FBI-1 interacts with MBD3 to recruit the Mi-2/NuRD-HDAC complex and BCoR and to silence p21WAF/CDKN1A by DNA methylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2013 Jul;41(13):6403-20. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt359. Epub 2013 May 8. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013. PMID: 23658227 Free PMC article.
-
NuRD blocks reprogramming of mouse somatic cells into pluripotent stem cells.Stem Cells. 2013 Jul;31(7):1278-86. doi: 10.1002/stem.1374. Stem Cells. 2013. PMID: 23533168
-
Phosphorylation-acetylation switch in the regulation of STAT1 signaling.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010 Feb 5;315(1-2):40-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2009.10.007. Epub 2009 Oct 29. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2010. PMID: 19879327 Review.
-
Interferons and their stimulated genes in the tumor microenvironment.Semin Oncol. 2014 Apr;41(2):156-73. doi: 10.1053/j.seminoncol.2014.02.002. Epub 2014 Feb 14. Semin Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24787290 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Immune evasion by cancer stem cells.Regen Ther. 2021 Mar 11;17:20-33. doi: 10.1016/j.reth.2021.02.006. eCollection 2021 Jun. Regen Ther. 2021. PMID: 33778133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Epigenetic Regulation in Plasticity of Tumor Immune Microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 2;12:640369. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.640369. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33868269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A bio-orthogonal linear ubiquitin probe identifies STAT3 as a direct substrate of OTULIN in glioblastoma.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Feb 22;51(3):1050-1066. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad002. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 36660824 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial Effect of PLK1 Inhibition with Temozolomide and Radiation in Glioblastoma.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 12;13(20):5114. doi: 10.3390/cancers13205114. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680264 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging roles of CircRNA-miRNA networks in cancer development and therapeutic response.Noncoding RNA Res. 2024 Sep 11;10:98-115. doi: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2024.09.006. eCollection 2025 Feb. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024. PMID: 39351450 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alvarado A.G., Thiagarajan P.S., Mulkearns-Hubert E.E., Silver D.J., Hale J.S., Alban T.J., Turaga S.M., Jarrar A., Reizes O., Longworth M.S., et al. . 2017. Glioblastoma Cancer Stem Cells Evade Innate Immune Suppression of Self-Renewal through Reduced TLR4 Expression. Cell Stem Cell. 20:450–461.e4. 10.1016/j.stem.2016.12.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

