The Pre-Treatment C-Reactive Protein Represents a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer Treated with Radiotherapy
- PMID: 32182693
- PMCID: PMC7139777
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12030626
The Pre-Treatment C-Reactive Protein Represents a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer Treated with Radiotherapy
Abstract
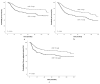
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the prognostic significance of the pre- treatment C-reactive protein (CRP) level in a cohort of 503 patients with oral and oropharyngeal cancer treated at a tertiary academic center between 2000 and 2017. Cancer-specific survival (CSS), overall survival (OS) and loco-regional control (LC) were calculated using Kaplan-Meier analysis. To evaluate the prognostic value of the CRP level for the clinical endpoints, univariate and multivariate Cox regression models were applied. The median follow-up period was 61 months. Patients were divided into elevated CRP (≥5 mg/L) and normal CRP groups, according to pre-treatment plasma levels. An increased CRP level was significantly associated with shorter CSS (p < 0.001, log-rank test), as well as with shorter OS (p < 0.001, log-rank test) and loco-regional control (p = 0.001, log-rank test). In addition, multivariate analysis identified CRP as an independent predictor for CSS (hazard ratio (HR) 1.59, 95% confidence interval (CI) 1.08-2.35; p = 0.020) as well as for OS (HR 1.62, 95%CI 1.17-2.24; p = 0.004) and LC (HR 1.50, 95%CI 1.06-2.14; p = 0.023). In subgroup analysis, Kaplan Meier curves revealed that an elevated pre-treatment CRP level was a consistent prognostic factor for poor CSS (p = 0.003, log-rank test), OS (p = 0.001, log-rank test), and LC (p = 0.028, log-rank test) in patients treated with definitive (chemo-) radiotherapy, whereas a significant association in patients undergoing surgery and postoperative radiotherapy was not detected. The pre-treatment CRP level seems to represent a prognostic factor for CSS, OS, and LC in patients with oral and oropharyngeal cancer, particularly in those treated with definitive (chemo-) radiotherapy. Additional large-scale prospective studies are warranted to confirm and extend our findings.
Keywords: C- reactive protein (CRP); biomarker; inflammation; oral and oropharyngeal cancer; outcome; prognostic factor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The elevated C-reactive protein level is associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer patients treated with radiotherapy.Eur J Cancer. 2015 Mar;51(5):610-9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 21. Eur J Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25618827
-
The Elevated Pre-Treatment C-Reactive Protein Predicts Poor Prognosis in Patients with Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer Treated with Neo-Adjuvant Radiochemotherapy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2020 Oct 2;10(10):780. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics10100780. Diagnostics (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33023215 Free PMC article.
-
The impact of elevated C-reactive protein level on the prognosis for oro-hypopharynx cancer patients treated with radiotherapy.Sci Rep. 2017 Dec 19;7(1):17805. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18233-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29259311 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic role of elevated preoperative systemic inflammatory markers in localized soft tissue sarcoma.Cancer Biomark. 2016;16(3):333-42. doi: 10.3233/CBM-160571. Cancer Biomark. 2016. PMID: 26835589 Review.
-
Prognostic role of serum C-reactive protein in esophageal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015 Jan 21;11:89-94. doi: 10.2147/TCRM.S70954. eCollection 2015. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015. PMID: 25653533 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Acute Phase Reaction and Its Prognostic Impact in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Single Biomarkers Including C-Reactive Protein Versus Biomarker Profiles.Biomedicines. 2020 Oct 14;8(10):418. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines8100418. Biomedicines. 2020. PMID: 33066437 Free PMC article.
-
Liquid Biopsy and Circulating Biomarkers for the Diagnosis of Precancerous and Cancerous Oral Lesions.Noncoding RNA. 2022 Aug 10;8(4):60. doi: 10.3390/ncrna8040060. Noncoding RNA. 2022. PMID: 36005828 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prognostic Impact of Serum CRP Level in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 29;12:889844. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.889844. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847918 Free PMC article.
-
Prospective Cohort Study Identifies Medical Predictors of Treatment-Related Oral Toxicities in Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer Patients.Dent J (Basel). 2024 Apr 1;12(4):89. doi: 10.3390/dj12040089. Dent J (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38668001 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic significance of pre- and post-treatment hematological biomarkers in patients with head and neck cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 8;13(1):3869. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-30584-1. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36890182 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Misawa K., Mima M., Satoshi Y., Misawa Y., Imai A., Mochizuki D., Nakagawa T., Kurokawa T., Oguro M., Ishikawa R., et al. Neuropeptide receptor genes GHSR and NMUR1 are candidate epigenetic biomarkers and predictors for surgically treated patients with oropharyngeal cancer. Sci. Rep. 2020;10:e1007. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-57920-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lu L., Wu Y., Feng M., Xue X., Fan Y. A novel sevenmiRNA prognostic model to predict overall survival in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma patients. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019;20:4340–4348. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

