Role of Microtubule-Associated Protein 1b in Urothelial Carcinoma: Overexpression Predicts Poor Prognosis
- PMID: 32182788
- PMCID: PMC7139768
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12030630
Role of Microtubule-Associated Protein 1b in Urothelial Carcinoma: Overexpression Predicts Poor Prognosis
Abstract
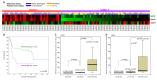
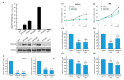
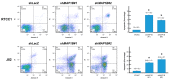
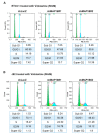
We sought to examine the relationship between microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) and the prognosis of urothelial carcinoma by assessing the microtubule bundle formation genes using a reappraisal transcriptome dataset of urothelial carcinoma (GSE31684). The result revealed that microtubule-associated protein 1b (MAP1B) is the most significant upregulated gene related to cancer progression. Real-time reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction was used to measure MAP1B transcription levels in urothelial carcinoma of the upper tract (UTUC) and the bladder (UBUC). Immunohistochemistry was conducted to detect MAP1B protein expression in 340 UTUC and 295 UBUC cases. Correlations of MAP1B expression with clinicopathological status, disease-specific survival, and metastasis-free survival were completed. To assess the oncogenic functions of MAP1B, the RTCC1 and J82 cell lines were stably silenced against their endogenous MAP1B expression. Study findings indicated that MAP1B overexpression was associated with adverse clinical features and could independently predict unfavorable prognostic effects, indicating its theranostic value in urothelial carcinoma.
Keywords: MAP1B; microtubule; prognosis; transcriptome; urothelial carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Lynch C.F., Davila J.A., Platz C.E. Cancer of the urinary bladder. In: Ries Y.J., Keel G.E., Eisner M.P., editors. SEER Survival Monograph: Cancer Survival Among Adults: US SEER Program, 1988–2001, Patient and Tumor Characteristics, National. Cancer Institute, SEER Program; Bethesda, MD, USA: 2007. pp. 193–202.
-
- Li C.C., Chang T.H., Wu W.J., Ke H.L., Huang S.P., Tsai P.C., Chang S.J., Shen J.T., Chou Y.H., Huang C.H. Significant predictive factors for prognosis of primary upper urinary tract cancer after radical nephroureterectomy in Taiwanese patients. Eur. Urol. 2008;54:1127–1134. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2008.01.054. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
- KMU-TP104E31, KMU-TP105G00, KMU-TP105G01, and KMU-TP105G02/Kaohsiung Medical University "Aim for the Top Universities,"
- MOHW105-TDU-B-212-134007l/Health and Welfare Surcharge of Tobacco Products, Ministry of Health and Welfare
- MOST103-2314-B-037-067-MY3/Ministry of Science and Technology
- KMUH101-1R47 and KMUH102-2R42/Kaohsiung Medical University Hospital
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

