Assessment of the Effect of Sorafenib on Omega-6 and Omega-3 Epoxyeicosanoid Formation in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 32182938
- PMCID: PMC7084535
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21051875
Assessment of the Effect of Sorafenib on Omega-6 and Omega-3 Epoxyeicosanoid Formation in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
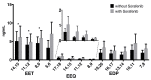
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer death. The multikinase inhibitor sorafenib is widely used for systemic therapy in advanced HCC. Sorafenib might affect epoxyeicosanoids, as it is also a potent inhibitor of the soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH), which catalyzes the conversion of epoxides derived from long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), such as arachidonic acid (AA) and omega-3 docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), into their corresponding diols. Experimental studies with AA-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) showed that they can promote tumor growth and metastasis, while DHA-derived 19,20-epoxydocosapentaenoic acid (19,20-EDP) was shown to have anti-tumor activity in mice. In this pilot study, we assessed the effect of sorafenib treatment on the presence of lipid mediators, such as EETs, in blood of the patients with HCC using the lipidomics technology. We found a significant increase in 11,12-EET and 14,15-EET levels in HCC patients treated with sorafenib. Furthermore, while not significant in this small sample set, the data presented indicate that sorafenib can also increase the level of omega-3 DHA-derived 19,20-EDP. While the effect on EETs might hamper the anti-tumor effect of sorafenib, we hypothesize that supplementation of DHA in sorafenib-treated HCC patients could increase the level of 19,20-EDP and thereby enhance its anti-tumor effect.
Keywords: EDP; EET; HCC; arachidonic acid; docosahexaenoic acid; hepatocellular carcinoma; n-3 PUFA; omega-3 fatty acids; soluble epoxide hydrolase; sorafenib.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sorafenib increases cytochrome P450 lipid metabolites in patient with hepatocellular carcinoma.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Mar 3;14:1124214. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1124214. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36937889 Free PMC article.
-
The factor in EDHF: Cytochrome P450 derived lipid mediators and vascular signaling.Vascul Pharmacol. 2016 Nov;86:31-40. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Mar 11. Vascul Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26975734 Review.
-
Inhibition of soluble epoxide hydrolase modulates inflammation and autophagy in obese adipose tissue and liver: role for omega-3 epoxides.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Jan 13;112(2):536-41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1422590112. Epub 2014 Dec 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25550510 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Pancreatic Carcinoma Growth Through Enhancing ω-3 Epoxy Polyunsaturated Fatty Acid Profile by Inhibition of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase.Anticancer Res. 2019 Jul;39(7):3651-3660. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13513. Anticancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31262891 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid mediators generated by the cytochrome P450-Epoxide hydrolase pathway.Adv Pharmacol. 2023;97:327-373. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2022.12.004. Epub 2023 Jan 19. Adv Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37236763 Review.
Cited by
-
Regioselective and Stereoselective Epoxidation of n-3 and n-6 Fatty Acids by Fungal Peroxygenases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Nov 25;10(12):1888. doi: 10.3390/antiox10121888. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34942990 Free PMC article.
-
Maximizing crustaceans (shrimp, crab, and lobster) by-products value for optimum valorization practices: A comparative review of their active ingredients, extraction, bioprocesses and applications.J Adv Res. 2024 Mar;57:59-76. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2023.11.002. Epub 2023 Nov 4. J Adv Res. 2024. PMID: 37931655 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Investigation of cell cytotoxic activity and molecular mechanism of 5β,19-epoxycucurbita-6,23(E)-diene-3β,19(R),25-triol isolated from Momordica charantia on hepatoma cells.Pharm Biol. 2022 Dec;60(1):1214-1223. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2022.2077766. Pharm Biol. 2022. PMID: 35760558 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid metabolism of hepatocellular carcinoma impacts targeted therapy and immunotherapy.World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023 Apr 15;15(4):617-631. doi: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i4.617. World J Gastrointest Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37123054 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Consequences of Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Deletion on Tumorigenesis and Metastasis in a Mouse Model of Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 1;22(13):7120. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137120. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34281173 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

