The Bradykinin-BDKRB1 Axis Regulates Aquaporin 4 Gene Expression and Consequential Migration and Invasion of Malignant Glioblastoma Cells via a Ca2+-MEK1-ERK1/2-NF-κB Mechanism
- PMID: 32182968
- PMCID: PMC7139930
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12030667
The Bradykinin-BDKRB1 Axis Regulates Aquaporin 4 Gene Expression and Consequential Migration and Invasion of Malignant Glioblastoma Cells via a Ca2+-MEK1-ERK1/2-NF-κB Mechanism
Abstract
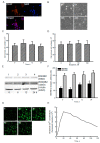
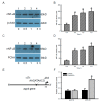
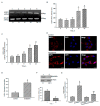
Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most common form of brain tumor and is very aggressive. Rapid migration and invasion of glioblastoma cells are two typical features driving malignance of GBM. Bradykinin functionally prompts calcium influx via activation of bradykinin receptor B1/B2 (BDKRB1/2). In this study, we evaluated the roles of bradykinin in migration and invasion of glioblastoma cells and the possible mechanisms. Expressions of aquaporin 4 (AQP4) mRNA and protein were upregulated in human glioblastomas. Furthermore, exposure of human U87 MG glioblastoma cells to bradykinin specifically increased levels of BDKRB1. Successively, bradykinin stimulated influx of calcium, phosphorylation of MEK1 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2, translocation and transactivation of nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-κB), and expressions of AQP4 mRNA and protein. Concomitantly, migration and invasion of human glioblastoma cells were elevated by bradykinin. Knocking-down BDKRB1 concurrently decreased AQP4 mRNA expression and cell migration and invasion. The bradykinin-induced effects were further confirmed in murine GL261 glioblastoma cells. Therefore, bradykinin can induce AQP4 expression and subsequent migration and invasion through BDKRB1-mediated calcium influx and subsequent activation of a MEK1-ERK1/2-NF-κB pathway. The bradykinin-BDKRB1 axis and AQP4 could be precise targets for treating GBM patients.
Keywords: MEK1-ERK1/2-NF-κB; aquaporin 4; bradykinin-BDKRB1 axis; calcium influx; cell migration/invasion; glioblastoma.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors of this paper declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Louis D.N., Perry A., Reifenberger G., Von Deimling A., Figarella-Branger D., Cavenee W.K., Ohgaki H., Wiestler O.D., Kleihues P., Ellison D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: A summary. Acta Neuropathol. 2016;131:803–820. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1545-1. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

