The Roles of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases in Cell-Cycle Progression and Therapeutic Strategies in Human Breast Cancer
- PMID: 32183020
- PMCID: PMC7139603
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21061960
The Roles of Cyclin-Dependent Kinases in Cell-Cycle Progression and Therapeutic Strategies in Human Breast Cancer
Abstract
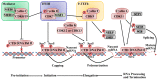
Cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) are serine/threonine kinases whose catalytic activities are regulated by interactions with cyclins and CDK inhibitors (CKIs). CDKs are key regulatory enzymes involved in cell proliferation through regulating cell-cycle checkpoints and transcriptional events in response to extracellular and intracellular signals. Not surprisingly, the dysregulation of CDKs is a hallmark of cancers, and inhibition of specific members is considered an attractive target in cancer therapy. In breast cancer (BC), dual CDK4/6 inhibitors, palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib, combined with other agents, were approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recently for the treatment of hormone receptor positive (HR+) advanced or metastatic breast cancer (A/MBC), as well as other sub-types of breast cancer. Furthermore, ongoing studies identified more selective CDK inhibitors as promising clinical targets. In this review, we focus on the roles of CDKs in driving cell-cycle progression, cell-cycle checkpoints, and transcriptional regulation, a highlight of dysregulated CDK activation in BC. We also discuss the most relevant CDK inhibitors currently in clinical BC trials, with special emphasis on CDK4/6 inhibitors used for the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive (ER+)/human epidermal growth factor 2-negative (HER2-) M/ABC patients, as well as more emerging precise therapeutic strategies, such as combination therapies and microRNA (miRNA) therapy.
Keywords: CDK inhibitor; breast cancer (BC); cell cycle; clinic therapy; cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

