The Repolarization Period during the Head-Up Tilt Test in Children with Vasovagal Syncope
- PMID: 32183460
- PMCID: PMC7143898
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17061908
The Repolarization Period during the Head-Up Tilt Test in Children with Vasovagal Syncope
Abstract
Background: Electrocardiography (ECG) and the head-up tilt test (HUTT) are vital in clinical work-up in children with vasovagal syncope (VVS). Ventricular repolarization parameters (QT) measured during the HUTT can be indicative of electrical instability; however, these parameters are not frequently assessed. This study aimed to investigate if ventricular repolarization parameters measured during the HUTT could be indicative of future ventricular arrhythmias in children with syncope.
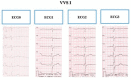
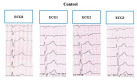
Methods: The shape and amplitude of the T-wave and parameters of the repolarization period (QT, QTpeak, Tpeak-Tend) were evaluated in a resting ECG performed on the first day of hospitalization and in ECGs performed during three phases of the HUTT.
Results: In the after-tilt phase of the HUTT, 19/30 children displayed a change in T-wave morphology. QTc was significantly longer in VVS I compared to that in VVS II patients, but not in the controls (p = 0.092).
Conclusions: We need further follow-up studies to establish the clinical importance of abnormal dynamics of the repolarization period in children with VVS and negative HUTT. Therefore, children with abnormal T-wave refraction and prolonged duration of the TpTe should remain under the care of a cardiological outpatient.
Keywords: electrocardiography; neurocardiogenic syncope; tilt test; vasovagal syncope; ventricular repolarization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prolongation of Electrocardiographic T Wave Parameters Recorded during the Head-Up Tilt Table Test as Independent Markers of Syncope Severity in Children.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Sep 4;17(18):6441. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17186441. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32899625 Free PMC article.
-
Repolarization disparity as a predictor of response to Head up Tilt-table Test in pediatric syncope.Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2021 Aug;44(8):1397-1403. doi: 10.1111/pace.14305. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol. 2021. PMID: 34181271
-
The Differences in the Diagnostic Profile in Children with Vasovagal Syncope between the Result of Head-Up Tilt Table Test.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jun 23;17(12):4524. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17124524. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32586003 Free PMC article.
-
Head-up Tilt Table Testing: a state-of-the-art review.Minerva Med. 2009 Aug;100(4):329-38. Minerva Med. 2009. PMID: 19749686 Review.
-
[Head-up tilt test--do we really know all about it?].Vnitr Lek. 2009 Oct;55(10):955-60. Vnitr Lek. 2009. PMID: 19947240 Review. Czech.
Cited by
-
Diagnostic Value of the TpTe Interval in Children with Ventricular Arrhythmias.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Nov 20;18(22):12194. doi: 10.3390/ijerph182212194. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34831949 Free PMC article.
-
Prolongation of Electrocardiographic T Wave Parameters Recorded during the Head-Up Tilt Table Test as Independent Markers of Syncope Severity in Children.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Sep 4;17(18):6441. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17186441. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32899625 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress on the predictive value of electrocardiographic indicators in the diagnosis and prognosis of children with vasovagal syncope.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Jul 22;9:916770. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.916770. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35935631 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive value of Tpeak-Tend interval of supine and orthostatic electrocardiogram in the diagnosis between psychogenic pseudosyncope and vasovagal syncope in children.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 17;14(1):28382. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-80110-0. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39551889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nowakowska E., Morka A., Szydłowski L. Syncope in children and adolescents as a sudden, transient, short-term and spontaneously reversible loss of consciousness caused by a decrease in cerebral perfusion. Pediatr. Med. Rodz. 2014;10:234–241. doi: 10.15557/PiMR.2014.0026. - DOI
-
- Brignole M., Menozzi C., Del Rosso A., Costa S. New classification of haemodynamics of vasovagal syncope: Beyond the VASIS classification. Analysis of the pre-syncopal phase of the tilt test without and with nitroglycerin challenge. Vasovagal Syncope International Study. Europace. 2000;2:66–76. doi: 10.1053/eupc.1999.0064. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

