ILK supports RhoA/ROCK-mediated contractility of human intestinal epithelial crypt cells by inducing the fibrillogenesis of endogenous soluble fibronectin during the spreading process
- PMID: 32183701
- PMCID: PMC7079544
- DOI: 10.1186/s12860-020-00259-0
ILK supports RhoA/ROCK-mediated contractility of human intestinal epithelial crypt cells by inducing the fibrillogenesis of endogenous soluble fibronectin during the spreading process
Abstract
Background: Fibronectin (FN) assembly into an insoluble fibrillar matrix is a crucial step in many cell responses to extracellular matrix (ECM) properties, especially with regards to the integrin-related mechanosensitive signaling pathway. We have previously reported that the silencing of expression of integrin-linked kinase (ILK) in human intestinal epithelial crypt (HIEC) cells causes significant reductions in proliferation and spreading through concomitantly acquired impairment of soluble FN deposition. These defects in ILK-depleted cells are rescued by growth on exogenous FN. In the present study we investigated the contribution of ILK in the fibrillogenesis of FN and its relation to integrin-actin axis signaling and organization.
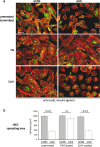
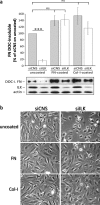
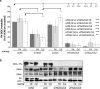
Results: We show that de novo fibrillogenesis of endogenous soluble FN is ILK-dependent. This function seemingly induces the assembly of an ECM that supports increased cytoskeletal tension and the development of a fully spread contractile cell phenotype. We observed that HIEC cell adhesion to exogenous FN or collagen-I (Col-I) is sufficient to restore fibrillogenesis of endogenous FN in ILK-depleted cells. We also found that optimal engagement of the Ras homolog gene family member A (RhoA) GTPase/Rho-associated kinase (ROCK-1, ROCK-2)/myosin light chain (MLC) pathway, actin ventral stress fiber formation, and integrin adhesion complex (IAC) maturation rely primarily upon the cell's capacity to execute FN fibrillogenesis, independent of any significant ILK input. Lastly, we confirm the integrin α5β1 as the main integrin responsible for FN assembly, although in ILK-depleted cells αV-class integrins expression is needed to allow the rescue of FN fibrillogenesis on exogenous substrate.
Conclusion: Our study demonstrates that ILK specifically induces the initiation of FN fibrillogenesis during cell spreading, which promotes RhoA/ROCK-dependent cell contractility and maturation of the integrin-actin axis structures. However, the fibrillogenesis process and its downstream effect on RhoA signaling, cell contractility and spreading are ILK-independent in human intestinal epithelial crypt cells.
Keywords: Actin stress fibers; Cell contractility; Epithelial cells; Fibrillogenesis; Fibronectin; ILK; IPP complex; Integrin; RhoA; α5β1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

