Relationships between academic self-efficacy, learning-related emotions, and metacognitive learning strategies with academic performance in medical students: a structural equation model
- PMID: 32183804
- PMCID: PMC7079530
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-020-01995-9
Relationships between academic self-efficacy, learning-related emotions, and metacognitive learning strategies with academic performance in medical students: a structural equation model
Abstract
Recognition of the factors affecting the medical students' academic success is one of the most important challenges and concerns in medical schools. Hence, this study aimed to investigate the mediating effects of metacognitive learning strategies and learning-related emotions in the relationship between academic self-efficacy with academic performance in medical students.
Methods: The present study was carried out on 279 students of medicine studying at Shiraz University of Medical Sciences. The students filled out three questionnaires: academic emotions (AEQ), metacognitive learning strategies, and academic self-efficacy questionnaires. The data were analyzed using SPSS and Smart PLS3.
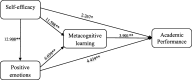
Results: The results of structural equation modeling revealed that the students' self-efficacy has an impact on their learning-related emotions and metacognitive learning strategies, and these, in turn, affect the students' academic performance. Moreover, learning-related emotions influence the metacognitive learning strategies, which in turn mediate the effect of emotions on academic performance.
Discussion: The results of this study revealed that metacognitive strategies and learning-related emotions could play a mediating role in the relationship between students' self-efficacy and academic performance.
Keywords: Academic performance; Academic self-efficacy; Learning-related emotions; Medical students; Metacognitive strategies.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Mitra Amini is a member of the editorial board for BMC Medical Education. They were blinded to the editorial process.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Medical students' motivation and academic performance: the mediating roles of self-efficacy and learning engagement.Med Educ Online. 2020 Dec;25(1):1742964. doi: 10.1080/10872981.2020.1742964. Med Educ Online. 2020. PMID: 32180537 Free PMC article.
-
Medical Student Progress Examination Performance and Its Relationship With Metacognition, Critical Thinking, and Self-Regulated Learning Strategies.Acad Med. 2021 Feb 1;96(2):278-284. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0000000000003766. Acad Med. 2021. PMID: 33003039
-
Relationship between metacognitive awareness and motivation to learn in medical students.BMC Med Educ. 2020 Oct 30;20(1):393. doi: 10.1186/s12909-020-02318-8. BMC Med Educ. 2020. PMID: 33126882 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring medical students' reflection on their learning: modification and validation of the motivated strategies for learning questionnaire (MSLQ).BMC Med Educ. 2018 Nov 22;18(1):274. doi: 10.1186/s12909-018-1384-y. BMC Med Educ. 2018. PMID: 30466427 Free PMC article.
-
Measuring Metacognitive Knowledge, Monitoring, and Control in the Pharmacy Classroom and Experiential Settings.Am J Pharm Educ. 2020 May;84(5):7730. doi: 10.5688/ajpe7730. Am J Pharm Educ. 2020. PMID: 32577037 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effect of self-efficacy and self-set grade goals on academic outcomes.Front Psychol. 2024 Mar 28;15:1324007. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1324007. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38605828 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Bullying on Positive Emotions and Their Effect as Mediators between Controllable Attributions of Success and Academic Performance.Children (Basel). 2023 May 24;10(6):929. doi: 10.3390/children10060929. Children (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37371161 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary study of the relationship between career choice motivation and understanding of professionalism in newly enrolled medical students in China: a cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2021 Feb 22;11(2):e041860. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-041860. BMJ Open. 2021. PMID: 33619186 Free PMC article.
-
Networks and Emotions in Cooperative Work: A Quasi-Experimental Study in University Nursing and Computer Engineering Students.Healthcare (Basel). 2020 Jul 20;8(3):220. doi: 10.3390/healthcare8030220. Healthcare (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32698453 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of the physician self-efficacy to manage emotional challenges Scale (PSMEC).BMC Med Educ. 2024 Mar 4;24(1):228. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05220-9. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38439059 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mega C, Ronconi L, De Beni R. What makes a good student? How emotions, self-regulated learning, and motivation contribute to academic achievement. J Educ Psychol. 2014;106(1):121. doi: 10.1037/a0033546. - DOI
-
- Sagheb MM, Amini M, Saber M, Moghadami M, Nabiei P, Khalili R, et al. Teaching Evidence-Based Medicine (EBM) to Undergraduate Medical Students through Flipped Classroom Approach. Shiraz E-Med J. 2018;19(2):1–6.
-
- Pekrun R, Goetz T, Titz W, Perry RP. Academic emotions in students' self-regulated learning and achievement: a program of qualitative and quantitative research. Educ Psychol. 2002;37(2):91–105. doi: 10.1207/S15326985EP3702_4. - DOI
-
- Pekrun R, Goetz T, Frenzel AC, Barchfeld P, Perry RP. Measuring emotions in students’ learning and performance: the achievement emotions questionnaire (AEQ) Contemp Educ Psychol. 2011;36(1):36–48. doi: 10.1016/j.cedpsych.2010.10.002. - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

