Angiopoietin-2 induces angiogenesis via exosomes in human hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 32183816
- PMCID: PMC7077328
- DOI: 10.1186/s12964-020-00535-8
Angiopoietin-2 induces angiogenesis via exosomes in human hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver cancer and is a highly vascularized solid tumor. Angiopoietin-2 (ANGPT2) has been described as an attractive target for antiangiogenic therapy. Exosomes are small extracellular vesicles secreted by most cell types and contribute to cell-to-cell communication by delivering functional cargo to recipient cells. The expression of ANGPT2 in tumor-derived exosomes remains unknown.
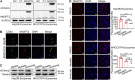
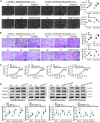
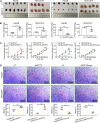
Methods: We detected the ANGPT2 expression in HCC-derived exosomes by immunoblotting, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunogold labeling, then observed exosomal ANGPT2 internalization and recycling by confocal laser scanning microscopy, co-immunoprecipitation and immunoblotting. We used two HCC cell lines (Hep3B and MHCC97H) to overexpress ANGPT2 by lentivirus infection or knockdown ANGPT2 by the CRISPR/Cas system, then isolated exosomes to coculture with human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and observed the angiogenesis by Matrigel microtubule formation assay, transwell migration assay, wound healing assay, cell counting kit-8 assay, immunoblotting and in vivo tumorigenesis assay.
Results: We found that HCC-derived exosomes carried ANGPT2 and delivered it into HUVECs by exosome endocytosis, this delivery led to a notable increase in angiogenesis by a Tie2-independent pathway. Concomitantly, we observed that HCC cell-secreted exosomal ANGPT2 was recycled by recipient HUVECs and might be reused. In addition, the CRISPR-Cas systems to knock down ANGPT2 significantly inhibited the angiogenesis induced by HCC cell-secreted exosomal ANGPT2, and obviously suppressed the epithelial-mesenchymal transition activation in HCC.
Conclusions: Taken together, these results reveal a novel pathway of tumor angiogenesis induced by HCC cell-secreted exosomal ANGPT2 that is different from the classic ANGPT2/Tie2 pathway. This way may be a potential therapeutic target for antiangiogenic therapy. Video Abstract.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Angiopoietin-2; CRISPR-Cas systems; Endocytosis; Epithelial-mesenchymal transition; Exosomes; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Recycling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

