Loss of BICD2 in muscle drives motor neuron loss in a developmental form of spinal muscular atrophy
- PMID: 32183910
- PMCID: PMC7076953
- DOI: 10.1186/s40478-020-00909-6
Loss of BICD2 in muscle drives motor neuron loss in a developmental form of spinal muscular atrophy
Abstract
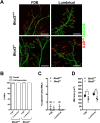
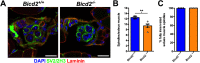
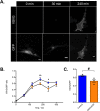
Autosomal dominant missense mutations in BICD2 cause Spinal Muscular Atrophy Lower Extremity Predominant 2 (SMALED2), a developmental disease of motor neurons. BICD2 is a key component of the cytoplasmic dynein/dynactin motor complex, which in axons drives the microtubule-dependent retrograde transport of intracellular cargo towards the cell soma. Patients with pathological mutations in BICD2 develop malformations of cortical and cerebellar development similar to Bicd2 knockout (-/-) mice. In this study we sought to re-examine the motor neuron phenotype of conditional Bicd2-/- mice. Bicd2-/- mice show a significant reduction in the number of large calibre motor neurons of the L4 ventral root compared to wild type mice. Muscle-specific knockout of Bicd2 results in a similar reduction in L4 ventral axons comparable to global Bicd2-/- mice. Rab6, a small GTPase required for the sorting of exocytic vesicles from the Trans Golgi Network to the plasma membrane is a major binding partner of BICD2. We therefore examined the secretory pathway in SMALED2 patient fibroblasts and demonstrated that BICD2 is required for physiological flow of constitutive secretory cargoes from the Trans Golgi Network to the plasma membrane using a VSV-G reporter assay. Together, these data indicate that BICD2 loss from muscles is a major driver of non-cell autonomous pathology in the motor nervous system, which has important implications for future therapeutic approaches in SMALED2.
Keywords: BICD2; DYNC1H1; Hereditary motor neuropathy; Muscle; SMALED2; Spinal muscular atrophy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Neveling K, Martinez-Carrera LA, Hölker I, Heister A, Verrips A, Hosseini-Barkooie SM, et al. Mutations in BICD2, which encodes a golgin and important motor adaptor, cause congenital autosomal-dominant spinal muscular atrophy. Am J Hum Genet. 2013;92:946–954. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2013.04.011. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

