Retrospective analysis of the possibility of predicting the COVID-19 outbreak from Internet searches and social media data, China, 2020
- PMID: 32183935
- PMCID: PMC7078825
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.10.2000199
Retrospective analysis of the possibility of predicting the COVID-19 outbreak from Internet searches and social media data, China, 2020
Abstract
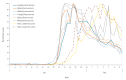
The peak of Internet searches and social media data about the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outbreak occurred 10-14 days earlier than the peak of daily incidences in China. Internet searches and social media data had high correlation with daily incidences, with the maximum r > 0.89 in all correlations. The lag correlations also showed a maximum correlation at 8-12 days for laboratory-confirmed cases and 6-8 days for suspected cases.
Keywords: Baidu Index; COVID-19; Google Trends; Internet surveillance; Weibo Index; coronavirus.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Novel Coronavirus Pneumonia Emergency Response Epidemiology Team [The epidemiological characteristics of an outbreak of 2019 novel coronavirus diseases (COVID-19) in China]. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2020;41(2):145-51. Chinese.
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). WHO Director-General's statement on IHR Emergency Committee on Novel Coronavirus (2019-nCoV). Geneva: WHO; 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-statement-...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
