Dendritic Cell Paucity Leads to Dysfunctional Immune Surveillance in Pancreatic Cancer
- PMID: 32183949
- PMCID: PMC7181337
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.02.008
Dendritic Cell Paucity Leads to Dysfunctional Immune Surveillance in Pancreatic Cancer
Abstract
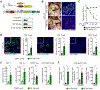
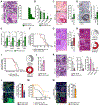
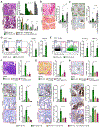
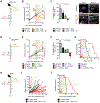
Here, we utilized spontaneous models of pancreatic and lung cancer to examine how neoantigenicity shapes tumor immunity and progression. As expected, neoantigen expression during lung adenocarcinoma development leads to T cell-mediated immunity and disease restraint. By contrast, neoantigen expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) results in exacerbation of a fibro-inflammatory microenvironment that drives disease progression and metastasis. Pathogenic TH17 responses are responsible for this neoantigen-induced tumor progression in PDAC. Underlying these divergent T cell responses in pancreas and lung cancer are differences in infiltrating conventional dendritic cells (cDCs). Overcoming cDC deficiency in early-stage PDAC leads to disease restraint, while restoration of cDC function in advanced PDAC restores tumor-restraining immunity and enhances responsiveness to radiation therapy.
Keywords: CD40; Flt3L; dendritic cell; immune surveillance; immunotherapy; neoantigen; pancreatic cancer; radiation therapy; vaccination.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Comment in
-
Context-Dependent Immune Responses Explain Pancreatic Cancer Immunoresistance.Cancer Cell. 2020 Mar 16;37(3):261-263. doi: 10.1016/j.ccell.2020.02.010. Cancer Cell. 2020. PMID: 32183944
-
Neoantigens Elicit Protumorigenic Immune Responses in Pancreatic Cancer.Cancer Discov. 2020 May;10(5):636. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-RW2020-047. Epub 2020 Mar 27. Cancer Discov. 2020. PMID: 32220924
-
DC deployment in pancreatic cancer.Nat Rev Immunol. 2020 May;20(5):276-277. doi: 10.1038/s41577-020-0298-1. Nat Rev Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32235867 No abstract available.
-
Rewiring local immune milieu by boosting dendritic cell for pancreatic cancer treatment.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020 Jul 2;5(1):114. doi: 10.1038/s41392-020-00225-4. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2020. PMID: 32616713 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Alam MS, Gaida MM, Bergmann F, Lasitschka F, Giese T, Giese NA, Hackert T, Hinz U, Hussain SP, Kozlov SV, and Ashwell JD (2015). Selective inhibition of the p38 alternative activation pathway in infiltrating T cells inhibits pancreatic cancer progression. Nature Medicine 21, 1337–1343. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bailey P, Chang DK, Nones K, Johns AL, Patch AM, Gingras MC, Miller DK, Christ AN, Bruxner TJ, Quinn MC, et al. (2016b). Genomic analyses identify molecular subtypes of pancreatic cancer. Nature 531, 47–52. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- S10 OD020136/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- K00 CA223043/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA203890/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA244938/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA091842/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP5 OD026427/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA177670/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F99 CA223043/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA196510/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA181745/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK052574/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR002345/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

