Effect of Topiramate on Morphine-induced Conditioned Place Preference (CPP) in Rats: Role of ERK and CREB Proteins in Hippocampus and Cerebral Cortex
- PMID: 32184865
- PMCID: PMC7059042
- DOI: 10.22037/ijpr.2019.1100873
Effect of Topiramate on Morphine-induced Conditioned Place Preference (CPP) in Rats: Role of ERK and CREB Proteins in Hippocampus and Cerebral Cortex
Abstract
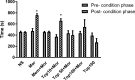
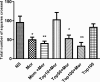
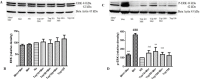
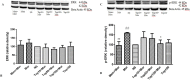
In this study, the effect of topiramate, as an antiepileptic drug, was evaluated on morphine craving in rats. The conditioned place preference (CPP) test was used for this purpose. Repeated administration of morphine (10 mg/kg, i.p. for 4 days) induced significant CPP. Administration of topiramate (50 and 100 mg/kg, i.p. for 4 days) with each morphine administration decreased the acquisition of morphine-induced CPP. At the next step, the levels of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK), p-ERK, cAMP responsive element binding (CREB), and p-CREB proteins were evaluated in hippocampus and cerebral cortex using western blot analysis. Following the repeated administration of morphine, the level of p-ERK protein markedly enhanced in both tissues, while topiramate could significantly reduce the phosphorylation of ERK in these brain regions. Additionally, the level of CREB and p-CREB proteins did not change in different groups. Memantine as a positive control reduced the acquisition of morphine-induced CPP. Also, memantine significantly decreased the level of p-ERK protein in hippocampus and cerebral cortex. These results demonstrated that topiramate can attenuate the acquisition of morphine-induced CPP in rats. This effect in part can be mediated through down regulation of p-ERK protein in hippocampus and cerebral cortex.
Keywords: CREB; Conditioned place preference; ERK; Morphine; Topiramate.
Figures

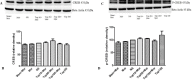
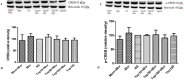
References
-
- Tabatabai SM, Dashti S, Doosti F, Hosseinzadeh H. Phytotherapy of opioid dependence and withdrawal syndrome: A review. Phytother. Res. 2014;28:811–30. - PubMed
-
- Veilleux JC, Colvin PJ, Anderson J, York C, Heinz AJ. A review of opioid dependence treatment: pharmacological and psychosocial interventions to treat opioid addiction. Clin. Psychol. Rev. 2010;30:155–66. - PubMed
-
- Bläsig J, Herz A, Reinhold K, Zieglgänsberger S. Development of physical dependence on morphine in respect to time and dosage and quantification of the precipitated withdrawal syndrome in rats. Psychopharmacologia . 1973;33:19–38. - PubMed
-
- Manzanedo C, Aguilar MA, RodríGuez-Arias M, Miñarro J. Effects of dopamine antagonists with different receptor blockade profiles on morphine-induced place preference in male mice. Behav. Brain Res. . 2001;121:189–97. - PubMed
-
- Olmstead MC, Franklin KB. The development of a conditioned place preference to morphine: effects of microinjections into various CNS sites. Behav. Neurosci. 1997;111:1324–34. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
