Combined Snail and E-cadherin Predicts Overall Survival of Cervical Carcinoma Patients: Comparison Among Various Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Proteins
- PMID: 32185181
- PMCID: PMC7058927
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2020.00022
Combined Snail and E-cadherin Predicts Overall Survival of Cervical Carcinoma Patients: Comparison Among Various Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Proteins
Abstract
Background: Activation of Snail and synergistic loss of E-cadherin are hallmark features of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which contributes to the metastasis phenotype of epithelial cancer cells. However, the prognostic impact of Snail and of its combination with E-cadherin and with other EMT prognostic markers has not yet been systematically studied in cervical carcinoma. This study aimed to explore the prognostic value of combined Snail and E-cadherin in patients with cervical carcinoma and compared it to the prognostic value of other EMT prognostic markers.
Methods: We retrospectively identified every initial diagnosis of cervical carcinoma among 203 patients treated at our hospital in China from January 2008 to March 2013. We examined the prognostic significance of Snail and other EMT protein markers, such as E-cadherin, Slug, ZEB1, Twist, Vimentin, and Survivin, by univariate and multivariate survival analyses.
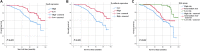
Results: Multivariate analyses showed that Snail and E-cadherin were significant biomarkers for overall survival (OS) in cervical carcinoma patients (HR, hazard ratio = 1.744, P = 0.036 and HR = 1.738, P = 0.047; respectively). Moreover, a combined index including Snail and E-cadherin showed enhanced prognostic value compared to that of Snail or E-cadherin alone. The present data demonstrate that Snail shows a negative correlation with E-cadherin (P < 0.001). High Snail expression and low E-cadherin expression were also more common in high tumor stages (P = 0.044 and P = 0.036; respectively), and lymph node metastasis (both P < 0.001). Moreover, Snail was a superior prognosis factor compared to Slug, ZEB1, Twist, Vimentin, and Survivin in cervical carcinoma.
Conclusion: Based on our results, Snail and E-cadherin may be considered as independent prognosis markers, and the combination of Snail and E-cadherin might improve the OS prediction accuracy for patients with cervical carcinoma.
Keywords: E-cadherin; EMT; Snail; cervical carcinoma; prognosis.
Copyright © 2020 Tian, Qi, Niu and Hu.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Prognostic value of Twist, Snail and E-cadherin expression in pathological N0 non-small-cell lung cancer: a retrospective cohort study.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018 Aug 1;54(2):237-245. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezy022. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018. PMID: 29415155
-
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Predicts Survival in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Pathol Oncol Res. 2020 Jul;26(3):1511-1518. doi: 10.1007/s12253-019-00731-z. Epub 2019 Aug 31. Pathol Oncol Res. 2020. PMID: 31471883
-
ZEB1 promotes the progression and metastasis of cervical squamous cell carcinoma via the promotion of epithelial-mesenchymal transition.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015 Sep 1;8(9):11258-67. eCollection 2015. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26617850 Free PMC article.
-
Co-expression of SNAIL and TWIST determines prognosis in estrogen receptor-positive early breast cancer patients.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012 May;133(1):49-59. doi: 10.1007/s10549-011-1684-y. Epub 2011 Jul 28. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012. PMID: 21796367
-
Genetic And Epigenetic Regulation Of E-Cadherin Signaling In Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2019 Oct 16;11:8947-8963. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S225606. eCollection 2019. Cancer Manag Res. 2019. PMID: 31802937 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GBA Regulates EMT/MET and Chemoresistance in Squamous Cell Carcinoma Cells by Modulating the Cellular Glycosphingolipid Profile.Cells. 2023 Jul 18;12(14):1886. doi: 10.3390/cells12141886. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37508550 Free PMC article.
-
Camptothecin improves sorafenib sensitivity by inhibiting Nrf2‑ARE pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Rep. 2023 Mar;49(3):55. doi: 10.3892/or.2023.8492. Epub 2023 Feb 3. Oncol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36734286 Free PMC article.
-
Role of lncRNA TPRG1-AS1 in the development of cervical squamous cell carcinoma and its prognostic value.Discov Oncol. 2024 Dec 18;15(1):754. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01654-1. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39692778 Free PMC article.
-
Snail-Family Proteins: Role in Carcinogenesis and Prospects for Antitumor Therapy.Acta Naturae. 2021 Jan-Mar;13(1):76-90. doi: 10.32607/actanaturae.11062. Acta Naturae. 2021. PMID: 33959388 Free PMC article.
-
Circular RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Emerging Functions to Clinical Significances.Front Oncol. 2021 May 14;11:667428. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.667428. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34055634 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bohrnsen F., Holzenburg J., Godek F., Kauffmann P., Moser N., Schliephake H. (2019). Influence of tumour necrosis factor alpha on epithelial-mesenchymal transition of oral cancer cells in co-culture with mesenchymal stromal cells. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 49 157–165. 10.1016/j.ijom.2019.06.001 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

