Evaluation of a new multipurpose whole-body CzT-based camera: comparison with a dual-head Anger camera and first clinical images
- PMID: 32185566
- PMCID: PMC7078403
- DOI: 10.1186/s40658-020-0284-5
Evaluation of a new multipurpose whole-body CzT-based camera: comparison with a dual-head Anger camera and first clinical images
Abstract
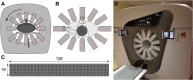
Background: Evaluate the physical performance of the VERITON CzT camera (Spectrum Dynamics, Caesarea, Israel) that benefits from new detection architecture enabling whole-body imaging compared to that of a conventional dual-head Anger camera.
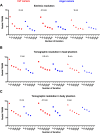
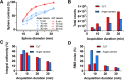
Methods: Different line sources and phantom measurements were performed on each system to evaluate spatial resolution, sensitivity, energy resolution and image quality with acquisition and reconstruction parameters similar to those used in clinical routine. Extrinsic resolution was assessed using 99mTc capillary sources placed successively in air, in a head and in a body phantom filled with background activity. Spectral acquisitions for various radioelements used in nuclear medicine (99mTc, 123I, 201Tl, 111In) were performed to evaluate energy resolution by computing the FWHM of the measured photoelectric peak. Tomographic sensitivity was calculated by recording the total number of counts detected during tomographic acquisition for a set of source geometries representative of different clinical situations. Sensitivity was also evaluated in focus mode for the CzT camera, which consisted of forcing detectors to collect data in a reduced field-of-view. Image quality was assessed with a Jaszczak phantom filled with 350 MBq of 99mTc and scanned on each system with 30-,20-,10- and 5-min acquisition times.
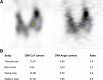
Results: Extrinsic and tomographic resolution in the brain and body phantoms at the centre of the FOV was estimated at 3.55, 7.72 and 6.66 mm for the CzT system and 2.47, 7.75 and 7.72 mm for the conventional system, respectively. The energy resolution measured at 140 keV was 5.46% versus 9.21% for the Anger camera and was higher in a same manner for all energy peaks tested. Tomographic sensitivity for a point source in air was estimated at 236 counts·s-1·MBq-1 and increased to 1159 counts·s-1·MBq-1 using focus mode, which was 1.6 times and 8 times greater than the sensitivity measured on the scintillation camera (144 counts·s-1·MBq-1). Head and body measurements also showed higher sensitivity for the CzT camera in particular with focus mode. The Jaszczak phantom showed high image contrast uniformity and a high signal-to-noise ratio on the CzT system, even when decreasing acquisition time by 6-fold. Representative clinical cases are shown to illustrate these results.
Conclusion: The CzT camera has a superior sensitivity, higher energy resolution and better image contrast than the conventional SPECT camera, whereas spatial resolution remains similar. Introduction of this new technology may change current practices in nuclear medicine such as decreasing acquisition time and activity injected to patient.
Keywords: Molecular imaging; Multipurpose CzT-camera; SPECT; Whole-body imaging.
Conflict of interest statement
DA and NA: travel grant (Spectrum dynamics), DA: honourarium (Spectrum dynamics).
The other authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
High-quality brain perfusion SPECT images may be achieved with a high-speed recording using 360° CZT camera.EJNMMI Phys. 2020 Nov 4;7(1):65. doi: 10.1186/s40658-020-00334-7. EJNMMI Phys. 2020. PMID: 33146804 Free PMC article.
-
Simulation studies of a full-ring, CZT SPECT system for whole-body imaging of 99m Tc and 177 Lu.Med Phys. 2023 Jun;50(6):3726-3737. doi: 10.1002/mp.16360. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Med Phys. 2023. PMID: 36916755 Free PMC article.
-
[Spatial Resolution and Uniformity of a Full-ring CZT SPECT/CT System: Comparison with a Conventional Anger-type SPECT/CT Instrument].Nihon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi. 2025;81(6). doi: 10.6009/jjrt.25-1527. Nihon Hoshasen Gijutsu Gakkai Zasshi. 2025. PMID: 40268386 Japanese.
-
Performance of cardiac cadmium-zinc-telluride gamma camera imaging in coronary artery disease: a review from the cardiovascular committee of the European Association of Nuclear Medicine (EANM).Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016 Dec;43(13):2423-2432. doi: 10.1007/s00259-016-3467-5. Epub 2016 Aug 19. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2016. PMID: 27542010 Review.
-
Research on the Technological Progress of CZT Array Detectors.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Jan 23;24(3):725. doi: 10.3390/s24030725. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38339441 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
3D dynamic diuretic renal scintigraphy using a hybrid whole body CZT SPECT/CT camera protocol in the evaluation of acute ureteric obstruction caused by ureteric stone.EJNMMI Rep. 2024 Sep 2;8(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s41824-024-00213-9. EJNMMI Rep. 2024. PMID: 39218826 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-pinhole collimator design in different numbers of projections for brain SPECT.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Sep 28;10:1211726. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1211726. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37841005 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of Imaging Small Animals on a 360° Whole-Body Cadmium Zinc Telluride SPECT Camera: a Phantom Study.Mol Imaging Biol. 2022 Dec;24(6):1018-1027. doi: 10.1007/s11307-022-01753-x. Epub 2022 Jul 14. Mol Imaging Biol. 2022. PMID: 35835951
-
Quantitative capabilities of commercial CZT SPECT-CT cameras with 99mTc.EJNMMI Phys. 2025 May 10;12(1):44. doi: 10.1186/s40658-025-00754-3. EJNMMI Phys. 2025. PMID: 40348848 Free PMC article.
-
Same same but different: dopamine transporter SPECT on scanners with CZT vs. NaI detectors.EJNMMI Res. 2023 Mar 22;13(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s13550-023-00973-8. EJNMMI Res. 2023. PMID: 36949290 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buechel RR, Herzog BA, Husmann L, Burger IA, Pazhenkottil AP, Treyer V, et al. Ultrafast nuclear myocardial perfusion imaging on a new gamma camera with semiconductor detector technique: first clinical validation. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2010;37(4):773–778. doi: 10.1007/s00259-009-1375-7. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

