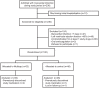
Multicap to improve adherence after acute coronary syndromes: results of a randomized controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 32186246
- PMCID: PMC7081461
- DOI: 10.1177/1753944720912071
Multicap to improve adherence after acute coronary syndromes: results of a randomized controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Background: Adherence to treatment after a myocardial infarction (MI) is poor, even in the early postinfarction period. Combining evidence-based drugs into a multicap could improve adherence in this population. No previous randomized trial assessing fixed-dose combination therapy has included patients early after a MI. We aimed to assess if a multicap containing four secondary prevention drugs increases adherence to treatment at 6 months after MI hospitalization. The study was designed as a randomized, parallel, open-label, controlled trial.
Methods: Patients were randomized within 7 days of a MI to either multicap or control group. The multicap group received a capsule containing aspirin, atenolol, ramipril, and simvastatin. The control group received each drug in separate pills. The primary outcome was adherence at 6 months. We also measured blood pressure, heart rate, serum cholesterol levels, C-reactive protein, and platelet aggregation.
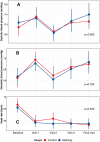
Results: The study was stopped prematurely when 100 patients were included for futility. At 6 months, 92 (95.8%) patients were adherent to medical treatment: 98.0% in the multicap group and 93.5% in the control group [relative risk (RR) 1.05; 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.96-1.14; p = 0.347]. There were no differences between groups in systolic blood pressure (p = 0.662), diastolic blood pressure (p = 0.784), heart rate (p = 0.533), total cholesterol (p = 0.760), LDL-c (p = 0.979), C-reactive protein (p = 0.399), or in the proportion of patients with adequate platelet aggregation inhibition (p = 0.600).
Conclusions: The study did not find any improvement in the adherence at 6 months after a MI with a multicap-based strategy (Multicap for Increase Adherence After Acute Myocardial Infarction; [ ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02271178]).
Keywords: coronary heart disease; fixed-dose combination therapy; multicap; myocardial infarction; polypill; secondary prevention.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Cholesterol Treatment Trialists’ (CTT) Collaboration, Fulcher J, O’Connell R, et al. Efficacy and safety of LDL-lowering therapy among men and women: meta-analysis of individual data from 174,000 participants in 27 randomised trials. Lancet 2015; 385: 1397–1405. - PubMed
-
- Rodrigues EJ, Eisenberg MJ, Pilote L. Effects of early and late administration of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors on mortality after myocardial infarction. Am J Med 2003; 115: 473–479. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials