Creating and screening natural product libraries
- PMID: 32186299
- PMCID: PMC8494140
- DOI: 10.1039/c9np00068b
Creating and screening natural product libraries
Abstract
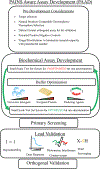
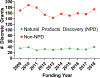
Covering: up to 2020The National Cancer Institute of the United States (NCI) has initiated a Cancer Moonshot program entitled the NCI Program for Natural Product Discovery. As part of this effort, the NCI is producing a library of 1 000 000 partially purified natural product fractions which are being plated into 384-well plates and provided to the research community free of charge. As the first 326 000 of these fractions have now been made available, this review seeks to describe the general methods used to collect organisms, extract those organisms, and create a prefractionated library. Importantly, this review also details both cell-based and cell-free bioassay methods and the adaptations necessary to those methods to productively screen natural product libraries. Finally, this review briefly describes post-screen dereplication and compound purification and scale up procedures which can efficiently identify active compounds and produce sufficient quantities of natural products for further pre-clinical development.
Conflict of interest statement
7 Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Newman DJ and Cragg GM, J. Nat. Prod, 2016, 79, 629–661. - PubMed
-
- Convention on Biological Diversity, Rio de Janeiro, 22nd May 1992, entered into force 29th Dec. 1993, https://www.cbd.int, accessed 2018.
-
- Koricheva J and Barton KE, in The Ecology of Plant Secondary Metabolites: From Genes to Global Processes, ed. Iason GR, Dicke M and Hartley SE, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 2012, pp. 34–55.
-
- United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, Montego Bay, 10th Dec. 1982, entered into force 16th Nov. 1994, http://www.un.org/depts/los/index.htm, accessed 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

