Involvement of long non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 32187055
- PMCID: PMC7176443
- DOI: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000755
Involvement of long non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
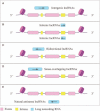
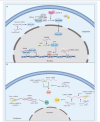
Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) plays a contributory role in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). In this review, we summarized the current findings of lncRNAs in RA, including cellular function and the potential mechanisms. Serum lncRNA levels are associated with serum proinflammatory cytokines and disease activity. LncRNAs regulate proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of RA fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs), modulate the differentiation of T lymphocytes and macrophages, and affect bone formation-destruction balance of chondrocytes. Besides, lncRNAs are involved in inflammation and cell motivation signaling pathways. In-depth research on lncRNAs may help elucidate the pathogenesis of RA and provides clues for novel treatment targets.
Figures

References
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature 2003; 423:356–361. doi: 10.1038/nature01661. - PubMed
-
- Brown AK, Conaghan PG, Karim Z, Quinn MA, Ikeda K, Peterfy CG, et al. An explanation for the apparent dissociation between clinical remission and continued structural deterioration in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2008; 58:2958–2967. doi: 10.1002/art.23945. - PubMed
-
- Rutherford AI, Subesinghe S, Hyrich KL, Galloway JB. Serious infection across biologic-treated patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2018; 77:905–910. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-212825. - PubMed
-
- Perkel JM. Visiting “noncodarnia”. Biotechniques 2013; 54:301.303-4. doi: 10.2144/000114037. - PubMed
-
- Liu J, Li D, Luo H, Zhu X. Circular RNAs: the star molecules in cancer. Mol Aspects Med 2019; 70:141–152. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2019.10.006. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

