High density of unrepaired genomic ribonucleotides leads to Topoisomerase 1-mediated severe growth defects in absence of ribonucleotide reductase
- PMID: 32187369
- PMCID: PMC7192613
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkaa103
High density of unrepaired genomic ribonucleotides leads to Topoisomerase 1-mediated severe growth defects in absence of ribonucleotide reductase
Abstract
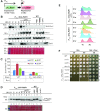
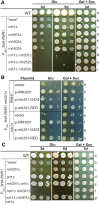
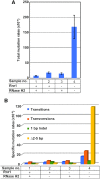
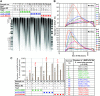
Cellular levels of ribonucleoside triphosphates (rNTPs) are much higher than those of deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs), thereby influencing the frequency of incorporation of ribonucleoside monophosphates (rNMPs) by DNA polymerases (Pol) into DNA. RNase H2-initiated ribonucleotide excision repair (RER) efficiently removes single rNMPs in genomic DNA. However, processing of rNMPs by Topoisomerase 1 (Top1) in absence of RER induces mutations and genome instability. Here, we greatly increased the abundance of genomic rNMPs in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by depleting Rnr1, the major subunit of ribonucleotide reductase, which converts ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides. We found that in strains that are depleted of Rnr1, RER-deficient, and harbor an rNTP-permissive replicative Pol mutant, excessive accumulation of single genomic rNMPs severely compromised growth, but this was reversed in absence of Top1. Thus, under Rnr1 depletion, limited dNTP pools slow DNA synthesis by replicative Pols and provoke the incorporation of high levels of rNMPs in genomic DNA. If a threshold of single genomic rNMPs is exceeded in absence of RER and presence of limited dNTP pools, Top1-mediated genome instability leads to severe growth defects. Finally, we provide evidence showing that accumulation of RNA/DNA hybrids in absence of RNase H1 and RNase H2 leads to cell lethality under Rnr1 depletion.
© The Author(s) 2020, Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research 2020.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RNases H1 and H2: guardians of the stability of the nuclear genome when supply of dNTPs is limiting for DNA synthesis.Curr Genet. 2020 Dec;66(6):1073-1084. doi: 10.1007/s00294-020-01086-8. Epub 2020 Sep 4. Curr Genet. 2020. PMID: 32886170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Studying Topoisomerase 1-Mediated Damage at Genomic Ribonucleotides.Methods Mol Biol. 2018;1703:241-257. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-7459-7_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 29177746
-
Mismatch repair-independent tandem repeat sequence instability resulting from ribonucleotide incorporation by DNA polymerase ε.DNA Repair (Amst). 2011 May 5;10(5):476-82. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2011.02.001. Epub 2011 Mar 16. DNA Repair (Amst). 2011. PMID: 21414850 Free PMC article.
-
Topoisomerase 1-mediated removal of ribonucleotides from nascent leading-strand DNA.Mol Cell. 2013 Mar 7;49(5):1010-5. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2012.12.021. Epub 2013 Jan 31. Mol Cell. 2013. PMID: 23375499 Free PMC article.
-
RNase H2-RED carpets the path to eukaryotic RNase H2 functions.DNA Repair (Amst). 2019 Dec;84:102736. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.102736. Epub 2019 Oct 23. DNA Repair (Amst). 2019. PMID: 31761672 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Human DNA topoisomerase I poisoning causes R loop-mediated genome instability attenuated by transcription factor IIS.Sci Adv. 2024 May 24;10(21):eadm8196. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adm8196. Epub 2024 May 24. Sci Adv. 2024. PMID: 38787953 Free PMC article.
-
RNase H2 degrades toxic RNA:DNA hybrids behind stalled forks to promote replication restart.EMBO J. 2023 Dec 1;42(23):e113104. doi: 10.15252/embj.2022113104. Epub 2023 Oct 19. EMBO J. 2023. PMID: 37855233 Free PMC article.
-
Cytotoxic mechanisms of pemetrexed and HDAC inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer cells involving ribonucleotides in DNA.Sci Rep. 2025 Jan 15;15(1):2082. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-86007-w. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39814799 Free PMC article.
-
AUF1 Recognizes 8-Oxo-Guanosine Embedded in DNA and Stimulates APE1 Endoribonuclease Activity.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023 Sep;39(7-9):411-431. doi: 10.1089/ars.2022.0105. Epub 2023 Apr 11. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2023. PMID: 36855946 Free PMC article.
-
A role for Rad5 in ribonucleoside monophosphate (rNMP) tolerance.Life Sci Alliance. 2021 Aug 18;4(10):e202000966. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202000966. Print 2021 Oct. Life Sci Alliance. 2021. PMID: 34407997 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stodola J.L., Burgers P.M.. Mechanism of lagging-strand DNA replication in eukaryotes. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017; 1042:117–133. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

