Metastasis-associated protein 1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by up-regulating Snail expression
- PMID: 32187849
- PMCID: PMC7294111
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15062
Metastasis-associated protein 1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by up-regulating Snail expression
Abstract
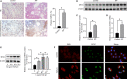
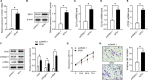
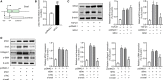
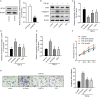
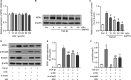
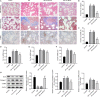
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive and usually fatal lung disease that lacking effective interventions. It is well known that aberrant activation of transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1) frequently promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in IPF. Metastasis-associated gene 1 (MTA1) has identified as an oncogene in several human tumours, and aberrant MTA1 expression has been related to the EMT regulation. However, its expression and function in IPF remain largely unexplored. Using a combination of in vitro and in vivo studies, we found that MTA1 was significantly up-regulated in bleomycin-induced fibrosis rats and TGF-β1-treated alveolar type Ⅱ epithelial (RLE-6TN) cells. Overexpression of MTA1 induced EMT of RLE-6TN cells, as well as facilitates cell proliferation and migration. In contrast, knockdown of MTA1 reversed TGF-β1-induced EMT of RLE-6TN cells. The pro-fibrotic action of MTA1 was mediated by increasing Snail expression through up-regulating Snail promoter activity. Moreover, inhibition of MTA1 effectively attenuated bleomycin-induced fibrosis in rats. Additionally, we preliminarily found astragaloside IV (ASV), which was previously validated having inhibitory effects on TGF-β1-induced EMT, could inhibit MTA1 expression in TGF-β1-treated RLE-6TN cells. These findings highlight the role of MTA1 in TGF-β1-mediated EMT that offer novel strategies for the prevention and treatment of IPF.
Keywords: astragaloside IV; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; metastasis-associated protein 1; snail.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Astragaloside IV modulates TGF-β1-dependent epithelial-mesenchymal transition in bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Sep;22(9):4354-4365. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13725. Epub 2018 Jul 4. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29971947 Free PMC article.
-
[Relationship between artesunate influence on the process of TGF-beta1 induced alveolar epithelial cells transform into mesenchymal cells and on idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis].Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2014 Jan;49(1):142-7. Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2014. PMID: 24783520 Chinese.
-
Nrf2 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition by suppressing snail expression during pulmonary fibrosis.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 16;6:38646. doi: 10.1038/srep38646. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27982105 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Transl Res. 2011 Apr;157(4):191-9. doi: 10.1016/j.trsl.2011.01.012. Epub 2011 Feb 4. Transl Res. 2011. PMID: 21420029 Review.
-
Molecular Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Fibrosis, with Focus on Pathways Related to TGF-β and the Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jun 5;22(11):6107. doi: 10.3390/ijms22116107. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34198949 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Estrogen attenuates TGF-β1-induced EMT in intrauterine adhesion by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020;53(8):e9794. doi: 10.1590/1414-431x20209794. Epub 2020 Jul 6. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2020. PMID: 32638833 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Exosomes in Pulmonary Fibrosis.Front Pharmacol. 2020 Dec 4;11:590972. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2020.590972. eCollection 2020. Front Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 33343360 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Scutellarin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis through inhibiting NF-κB/NLRP3-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition and inflammation.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Nov 13;11(11):978. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-03178-2. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 33188176 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: A Major Pathogenic Driver in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis?Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Nov 13;56(11):608. doi: 10.3390/medicina56110608. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 33202716 Free PMC article.
-
Untapping the Potential of Astragaloside IV in the Battle Against Respiratory Diseases.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023 Jul 3;17:1963-1978. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S416091. eCollection 2023. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2023. PMID: 37426627 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ng B, Dong J, D'Agostino G, et al. Interleukin‐11 is a therapeutic target in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(511):eaaw1237. - PubMed
-
- Miao C, Xiong Y, Zhang G, Chang J. MicroRNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, new research progress and their pathophysiological implication. Exp Lung Res. 2018;44:178‐190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

