Metastasis-associated protein 1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by up-regulating Snail expression
- PMID: 32187849
- PMCID: PMC7294111
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.15062
Metastasis-associated protein 1 promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis by up-regulating Snail expression
Abstract
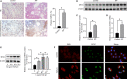
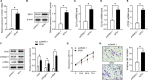
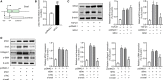
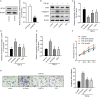
Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is a progressive and usually fatal lung disease that lacking effective interventions. It is well known that aberrant activation of transforming growth factor-beta1 (TGF-β1) frequently promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in IPF. Metastasis-associated gene 1 (MTA1) has identified as an oncogene in several human tumours, and aberrant MTA1 expression has been related to the EMT regulation. However, its expression and function in IPF remain largely unexplored. Using a combination of in vitro and in vivo studies, we found that MTA1 was significantly up-regulated in bleomycin-induced fibrosis rats and TGF-β1-treated alveolar type Ⅱ epithelial (RLE-6TN) cells. Overexpression of MTA1 induced EMT of RLE-6TN cells, as well as facilitates cell proliferation and migration. In contrast, knockdown of MTA1 reversed TGF-β1-induced EMT of RLE-6TN cells. The pro-fibrotic action of MTA1 was mediated by increasing Snail expression through up-regulating Snail promoter activity. Moreover, inhibition of MTA1 effectively attenuated bleomycin-induced fibrosis in rats. Additionally, we preliminarily found astragaloside IV (ASV), which was previously validated having inhibitory effects on TGF-β1-induced EMT, could inhibit MTA1 expression in TGF-β1-treated RLE-6TN cells. These findings highlight the role of MTA1 in TGF-β1-mediated EMT that offer novel strategies for the prevention and treatment of IPF.
Keywords: astragaloside IV; epithelial-mesenchymal transition; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; metastasis-associated protein 1; snail.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
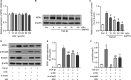
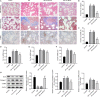
References
-
- Ng B, Dong J, D'Agostino G, et al. Interleukin‐11 is a therapeutic target in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Sci Transl Med. 2019;11(511):eaaw1237. - PubMed
-
- Miao C, Xiong Y, Zhang G, Chang J. MicroRNAs in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, new research progress and their pathophysiological implication. Exp Lung Res. 2018;44:178‐190. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

