Comprehensive Genome Analysis on the Novel Species Sphingomonas panacis DCY99T Reveals Insights into Iron Tolerance of Ginseng
- PMID: 32188055
- PMCID: PMC7139845
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21062019
Comprehensive Genome Analysis on the Novel Species Sphingomonas panacis DCY99T Reveals Insights into Iron Tolerance of Ginseng
Abstract
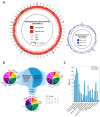
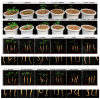
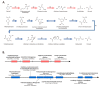
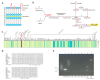
Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria play vital roles not only in plant growth, but also in reducing biotic/abiotic stress. Sphingomonas panacis DCY99T is isolated from soil and root of Panax ginseng with rusty root disease, characterized by raised reddish-brown root and this is seriously affects ginseng cultivation. To investigate the relationship between 159 sequenced Sphingomonas strains, pan-genome analysis was carried out, which suggested genomic diversity of the Sphingomonas genus. Comparative analysis of S. panacis DCY99T with Sphingomonas sp. LK11 revealed plant growth-promoting potential of S. panacis DCY99T through indole acetic acid production, phosphate solubilizing, and antifungal abilities. Detailed genomic analysis has shown that S. panacis DCY99T contain various heavy metals resistance genes in its genome and the plasmid. Functional analysis with Sphingomonas paucimobilis EPA505 predicted that S. panacis DCY99T possess genes for degradation of polyaromatic hydrocarbon and phenolic compounds in rusty-ginseng root. Interestingly, when primed ginseng with S. panacis DCY99T during high concentration of iron exposure, iron stress of ginseng was suppressed. In order to detect S. panacis DCY99T in soil, biomarker was designed using spt gene. This study brings new insights into the role of S. panacis DCY99T as a microbial inoculant to protect ginseng plants against rusty root disease.
Keywords: Biotic stress; Iron stress; Panax ginseng; Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria; Sphingomonas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Shahid M., Khalid S., Abbas G., Shahid N., Nadeem M., Sabir M., Aslam M., Dumat C. Crop Production and Global Environmental Issues. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2015. Heavy metal stress and crop productivity; pp. 1–25.
-
- Bodek I. Environmental Inorganic Chemistry: Properties, Processes, and Estimation Methods. Pergamon Press; Pergamon, Turkey: 1988.
-
- De Dorlodot S., Lutts S., Bertin P. Effects of ferrous iron toxicity on the growth and mineral composition of an interspecific rice. J. Plant Nutr. 2005;28:1–20. doi: 10.1081/PLN-200042144. - DOI
-
- Zhang Y., Wang Q., Xu C., Sun H., Wang J., Li L. Iron (Fe2+)-induced toxicity produces morphological and physiological changes in roots in Panax ginseng grown in hydroponics. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2016;98:630–637. doi: 10.1080/02772248.2015.1133385. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

