Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Metal-Containing Linseed Oil-Based Waterborne Urethane Oil Wood Coatings
- PMID: 32188061
- PMCID: PMC7183048
- DOI: 10.3390/polym12030663
Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of Metal-Containing Linseed Oil-Based Waterborne Urethane Oil Wood Coatings
Abstract
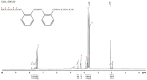
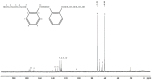
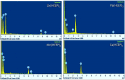
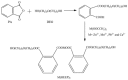
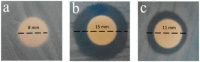
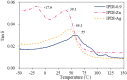
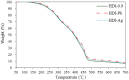
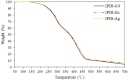
In this study, the antimicrobial agents of mono(hydroxyethoxyethyl)phthalate (M(HEEP)2) with different metal of M = Zn, Mn, Pb, and Ca were synthesized from diethylene glycol (DEG), phthalic anhydride (PA), and divalent metal acetates including calcium acetate, zinc acetate, manganese acetate, and lead acetate, respectively. The waterborne urethane oil (WUO) dispersions synthesized from linseed oil, diisocyanates (hexamethylene diisocyanate (HDI) and isophorone diisocyanate (IPDI)), dimethylolpropionic acid at NCO/OH molars of 0.9, by acetone processing method were described as in our previous report. The M(HEEP)2 antimicrobial agents as well as the commercial nanosilver powder were added into WUO dispersions as the antimicrobial coatings. The effects of various antimicrobial agents and dosages (0.0, 0.2, 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 2.0, and 4.0 phr) on antimicrobial activity of WUO films against gram-negative bacterium of Escherichia coli, gram-positive bacterium of Staphylococcus aureus, brown-rot fungus of Gloeophyllum trabeum, and white-rot fungus of Lenzites betulina were assessed. In addition, the film properties of the best antimicrobial WUO coatings were also examined. The results showed that the antimicrobial agents of mono(hydroxyethoxyethyl) phthalate M(HEEP)2 (M = Zn, Mn, Pb, and Ca) powders should certainly be synthesized by FTIR, 1H-NMR, 13C-NMR, and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) identifications and the yields of them were 43-55%. The results also revealed that the WUO film synthesizing with HDI films containing Zn(HEEP)2 of 2.0 phr and Pb(HEEP)2 of 0.4 phr had the best antibacterial activity for E. coli and S. aureus, respectively. The IPDI films containing Zn(HEEP)2 of 1.0 phr had the best antibacterial activity for both E. coli and S. aureus. For antifungal activity, the WUO film synthesizing with HDI films containing Pb(HEEP)2 of 0.8 phr and Zn(HEEP)2 of 2.0 phr as well as IPDI films containing Mn(HEEP)2 of 0.2 phr and Zn(HEEP)2 of 4.0 phr had the best performances against G. trabeum and L. betulina, respectively. Comparing with commercial nanoAg powder, the Zn(HEEP)2 and Pb(HEEP)2 had a superior antifungal efficiency for G. trabeum and L. betulina, while it had a slightly inferior efficiency in the antibacterial activity for E. coli and S. aureus. On the properties of WUO films, adding metal-containing antimicrobial agents could slightly enhance the thermal stability, but lowered the gloss of all films, however, the Tg value increased for HDI film and decreased for IPDI film. In addition to this, they had no significant difference in the film properties including hardness, impact resistance, bending resistance, adhesion, mass retention, and light-fastness between the WUO films with and without adding antimicrobial agents.
Keywords: antimicrobial activity; linseed oil; mono(hydroxyethoxyethyl) phthalate; waterborne urethane oil; wood coatings.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Metal-Containing Ultraviolet-Cured Wood Floor Coatings.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Sep 7;13(18):3022. doi: 10.3390/polym13183022. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34577922 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of Linseed Oil-Based Waterborne Urethane Oil Wood Coatings.Polymers (Basel). 2018 Nov 7;10(11):1235. doi: 10.3390/polym10111235. Polymers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30961160 Free PMC article.
-
Syntheses and Characteristics of Urushiol-Based Waterborne UV-Cured Wood Coatings.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Nov 19;13(22):4005. doi: 10.3390/polym13224005. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34833302 Free PMC article.
-
Chitosan films and coatings containing essential oils: The antioxidant and antimicrobial activity, and application in food systems.Food Res Int. 2016 Nov;89(Pt 1):117-128. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2016.10.004. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Food Res Int. 2016. PMID: 28460897 Review.
-
Nano-enabled antimicrobial thin films: design and mechanism of action.RSC Adv. 2024 Feb 9;14(8):5290-5308. doi: 10.1039/d3ra07884a. eCollection 2024 Feb 7. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38357038 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and Antibacterial Activity of Metal-Containing Ultraviolet-Cured Wood Floor Coatings.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Sep 7;13(18):3022. doi: 10.3390/polym13183022. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34577922 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in Environment-Friendly Polyurethanes from Polyols Recovered from the Recycling and Renewable Resources: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Jul 2;16(13):1889. doi: 10.3390/polym16131889. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39000744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Influence of Reaction Parameters on the Gelation of Silanised Linseed Oil.Materials (Basel). 2020 Nov 26;13(23):5376. doi: 10.3390/ma13235376. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33256253 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhang C., Xia Y., Chen R., Huh S., Johnston P.A., Kessler M.R. Soy-Castor Oil Based Polyols Prepared Using a Solvent-free and Catalyst-free Method and Polyurethanes. Therefrom. Green Chem. 2013;15:1477–1484. doi: 10.1039/c3gc40531a. - DOI
-
- Xia Y., Larock R.C. Vegetable Oil-based Polymeric Materials: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications. Green Chem. 2010;12:1893–1909. doi: 10.1039/c0gc00264j. - DOI
-
- Li S., Xu C., Yang W., Tang Q. Thermoplastic Polyurethanes Stemming from Castor Oil: Green Synthesis and Their Application in Wood Bonding. Coatings. 2017;7:159.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

