Quinolone Complexes with Lanthanide Ions: An Insight into their Analytical Applications and Biological Activity
- PMID: 32188087
- PMCID: PMC7144119
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25061347
Quinolone Complexes with Lanthanide Ions: An Insight into their Analytical Applications and Biological Activity
Abstract
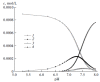
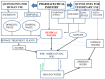
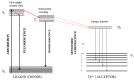
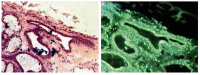
Quinolones comprise a series of synthetic bactericidal agents with a broad spectrum of activity and good bioavailability. An important feature of these molecules is their capacity to bind metal ions in complexes with relevant biological and analytical applications. Interestingly, lanthanide ions possess extremely attractive properties that result from the behavior of the internal 4f electrons, behavior which is not lost upon ionization, nor after coordination. Subsequently, a more detailed discussion about metal complexes of quinolones with lanthanide ions in terms of chemical and biological properties is made. These complexes present a series of characteristics, such as narrow and highly structured emission bands; large gaps between absorption and emission wavelengths (Stokes shifts); and long excited-state lifetimes, which render them suitable for highly sensitive and selective analytical methods of quantitation. Moreover, quinolones have been widely prescribed in both human and animal treatments, which has led to an increase in their impact on the environment, and therefore to a growing interest in the development of new methods for their quantitative determination. Therefore, analytical applications for the quantitative determination of quinolones, lanthanide and miscellaneous ions and nucleic acids, along with other applications, are reviewed here.
Keywords: biological activity; fluoroquinolones; lanthanides; metal complexes; quantitative determination.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metal complexes of quinolone antibiotics and their applications: an update.Molecules. 2013 Sep 11;18(9):11153-97. doi: 10.3390/molecules180911153. Molecules. 2013. PMID: 24029748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isoquinoline-based lanthanide complexes: bright NIR optical probes and efficient MRI agents.Inorg Chem. 2012 Feb 20;51(4):2522-32. doi: 10.1021/ic202446e. Epub 2012 Jan 10. Inorg Chem. 2012. PMID: 22233349
-
Lanthanide Chemistry: From Coordination in Chemical Complexes Shaping Our Technology to Coordination in Enzymes Shaping Bacterial Metabolism.Inorg Chem. 2016 Oct 17;55(20):10083-10089. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.6b00919. Epub 2016 Sep 2. Inorg Chem. 2016. PMID: 27588435 Review.
-
Dual targeting of topoisomerase IV and gyrase to reduce mutant selection: direct testing of the paradigm by using WCK-1734, a new fluoroquinolone, and ciprofloxacin.Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005 May;49(5):1949-56. doi: 10.1128/AAC.49.5.1949-1956.2005. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2005. PMID: 15855518 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis and structural properties of lanthanide complexes formed with tropolonate ligands.Inorg Chem. 2007 Aug 6;46(16):6473-82. doi: 10.1021/ic7005343. Epub 2007 Jul 10. Inorg Chem. 2007. PMID: 17622139
Cited by
-
New terbium complex as a luminescent probe for determination of chlorogenic acid in green coffee and roasted coffee infusions.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023 Jan;415(2):235-244. doi: 10.1007/s00216-022-04411-x. Epub 2022 Nov 15. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023. PMID: 36380245 Free PMC article.
-
A Study on Repositioning Nalidixic Acid via Lanthanide Complexation: Synthesis, Characterization, Cytotoxicity and DNA/Protein Binding Studies.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 17;15(8):1010. doi: 10.3390/ph15081010. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015158 Free PMC article.
-
Albumin/Thiacalix[4]arene Nanoparticles as Potential Therapeutic Systems: Role of the Macrocycle for Stabilization of Monomeric Protein and Self-Assembly with Ciprofloxacin.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 2;23(17):10040. doi: 10.3390/ijms231710040. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077448 Free PMC article.
-
Ruthenium Complexes in the Fight against Pathogenic Microorganisms. An Extensive Review.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jun 13;13(6):874. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13060874. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34199283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rare-Earth Metal Complexes of the Antibacterial Drug Oxolinic Acid: Synthesis, Characterization, DNA/Protein Binding and Cytotoxicity Studies.Molecules. 2020 Nov 19;25(22):5418. doi: 10.3390/molecules25225418. Molecules. 2020. PMID: 33228104 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

