Enhanced Adipose Expression of Interferon Regulatory Factor (IRF)-5 Associates with the Signatures of Metabolic Inflammation in Diabetic Obese Patients
- PMID: 32188105
- PMCID: PMC7140673
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9030730
Enhanced Adipose Expression of Interferon Regulatory Factor (IRF)-5 Associates with the Signatures of Metabolic Inflammation in Diabetic Obese Patients
Abstract
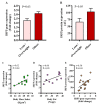
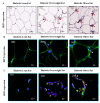
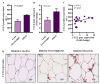
: Interferon regulatory factors (IRFs) are emerging as the metabolic transcriptional regulators in obesity/type-2 diabetes (T2D). IRF5 is implicated with macrophage polarization toward the inflammatory M1-phenotype, nonetheless, changes in the adipose expression of IRF5 in T2D and relationship of these changes with other markers of adipose inflammation remain unclear. Therefore, we determined the IRF5 gene expression in subcutaneous adipose tissue samples from 46 T2D patients including 35 obese (Body Mass Index/BMI 33.83 ± 0.42kg/m2) and 11 lean/overweight individuals (BMI 27.55 ± 0.46kg/m2) using real-time qRT-PCR. IRF5 protein expression was assessed using immunohistochemistry and confocal microscopy. Fasting plasma glucose, insulin, HbA1c, C-reactive protein, cholesterol, low- and high-density lipoproteins (LDL/HDL), and triglycerides were measured using commercial kits. IRF5 gene expression was compared with that of signature inflammatory markers and several clinico-metabolic indicators. The data (mean ± SEM) show the enhanced adipose IRF5 gene (p = 0.03) and protein (p = 0.05) expression in obese compared to lean/overweight diabetic patients. Adipose IRF5 transcripts in diabetic obese individuals associated positively with those of TNF-α, IL-18, IL-23A, CXCL8, CCL2, CCL7, CCR1/5, CD11c, CD68, CD86, TLR4/7/10, Dectin-1, FGL-2, MyD88, NF-κB, IRF3, and AML1 (p < 0.05). In diabetic lean/overweight subjects, IRF5 expression associated with BMI, body fat %age, glucose, insulin, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR, C-reactive protein (CRP), IL-5, and IL-1RL1 expression; while in all T2D patients, IRF5 expression correlated with that of IRF4, TLR2/8, and CD163. In conclusion, upregulated adipose tissue IRF5 expression in diabetic obese patients concurs with the inflammatory signatures and it may represent a potential marker for metabolic inflammation in obesity/T2D.
Keywords: Interferon regulatory factor-5; adipose tissue; metabolic inflammation; obesity; type-2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Increased Adipose Tissue Expression of Interferon Regulatory Factor (IRF)-5 in Obesity: Association with Metabolic Inflammation.Cells. 2019 Nov 11;8(11):1418. doi: 10.3390/cells8111418. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31718015 Free PMC article.
-
Repetitive Intermittent Hyperglycemia Drives the M1 Polarization and Inflammatory Responses in THP-1 Macrophages Through the Mechanism Involving the TLR4-IRF5 Pathway.Cells. 2020 Aug 12;9(8):1892. doi: 10.3390/cells9081892. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32806763 Free PMC article.
-
Increased adipose tissue expression of IL-18R and its ligand IL-18 associates with inflammation and insulin resistance in obesity.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2017 Sep;5(3):318-335. doi: 10.1002/iid3.170. Epub 2017 May 15. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2017. PMID: 28508444 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Diverse mechanisms of IRF5 action in inflammatory responses.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018 Jun;99:38-42. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2018.03.012. Epub 2018 Mar 22. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29578052 Review.
-
Transcriptional control of metabolism by interferon regulatory factors.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2024 Oct;20(10):573-587. doi: 10.1038/s41574-024-00990-0. Epub 2024 May 20. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38769435 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CCL7 as a novel inflammatory mediator in cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, and kidney disease.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 Sep 15;21(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01626-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 36109744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Caveolin-1 rs1997623 Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Creates a New Binding Site for the Early B-Cell Factor 1 That Instigates Adipose Tissue CAV1 Protein Overexpression.Cells. 2022 Dec 6;11(23):3937. doi: 10.3390/cells11233937. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36497195 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Gene Expression of Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue among Lean, Obese, and after RYGB (Different Timepoints): Systematic Review and Analysis.Nutrients. 2022 Nov 21;14(22):4925. doi: 10.3390/nu14224925. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36432612 Free PMC article.
-
A Missing Puzzle in Preclinical Studies-Are CCR2, CCR5, and Their Ligands' Roles Similar in Obesity-Induced Hypersensitivity and Diabetic Neuropathy?-Evidence from Rodent Models and Clinical Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 21;25(20):11323. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011323. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457105 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Involvement of Interleukin-1 Receptor-Associated Kinase 4 and Interferon Regulatory Factor 5 in the Immunopathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Implications for the Treatment of COVID-19.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 7;12:638446. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.638446. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33936053 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Greevenbroek M.M., Schalkwijk C.G., Stehouwer C.D. Obesity-associated low-grade inflammation in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Causes and consequences. Neth. J. Med. 2013;71:174–187. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

