How much of skin improvement over time in systemic sclerosis is due to normal ageing? A prospective study with shear-wave elastography
- PMID: 32188488
- PMCID: PMC7079468
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-020-02150-x
How much of skin improvement over time in systemic sclerosis is due to normal ageing? A prospective study with shear-wave elastography
Abstract
Background: Measurement of skin involvement is essential for the diagnosis and assessment of prognosis and disease progression in systemic sclerosis (SSc). The modified Rodnan skin score (mRSS) is the gold standard measure of skin thickness, but it has been criticised for the lack of objectivity, poor inter-observer reproducibility and lack of sensitivity to change. Recently, shear-wave elastography (SWE) emerged as a promising tool for the objective and quantitative assessment of the skin in SSc patients. However, no studies have evaluated its sensitivity to change over time.
Objective: To assess changes in skin stiffness in SSc patients using SWE during a 5-year follow-up.
Methods: Skin stiffness [i.e. shear-wave velocity values (SWV) in metres per second] was assessed by SWE ultrasound (using virtual touch image quantification) at the 17 sites of the mRSS, in each participant, at baseline and follow-up. mRSS was performed at both time points. Differences between groups were analysed using the related-samples Wilcoxon signed-rank test and the Mann-Whitney U test.
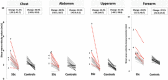
Results: We included 21 patients [85.7% females; mean age 56.3 (10.4) years at baseline, 57.1% with limited SSc] and 15 healthy controls [73.3% females; mean age 53.6 (14.1) years)]. The median follow-up was 4.9 (0.4) years. Skin stiffness decreased significantly at all Rodnan sites (p ≤ 0.001) (except in the fingers), in SSc patients, over time. The same phenomenon occurred in controls, but to a lesser degree, in terms of percentage change. The percentage reduction in skin stiffness varied in the different Rodnan sites and in different phases of the disease. In addition, SWV values also decreased significantly in 15/16 skin sites with local normal Rodnan at baseline, whereas local Rodnan skin score only changed significantly in the upper arm (p = 0.046) and forearm (p = 0.026).
Conclusion: This study provides first-time evidence suggesting that skin SWV values are more sensitive to change over time than mRSS and reduce significantly over time in SSc and normal controls.
Keywords: Shear-wave elastography; Skin; Stiffness; Systemic sclerosis; Ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative Assessment of Skin Stiffness Using Ultrasound Shear Wave Elastography in Systemic Sclerosis.Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019 Apr;45(4):902-912. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2018.11.015. Epub 2019 Jan 18. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 30665723
-
A preliminary study using virtual touch imaging and quantification for the assessment of skin stiffness in systemic sclerosis.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016 Sep-Oct;34 Suppl 100(5):137-141. Epub 2016 Feb 25. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 26939859
-
Quantification of skin stiffness in patients with systemic sclerosis using real-time shear wave elastography: a preliminary study.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018 Jul-Aug;36 Suppl 113(4):118-125. Epub 2018 Jun 11. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 29998836
-
High-resolution ultrasound imaging of skin involvement in systemic sclerosis: a systematic review.Rheumatol Int. 2021 Feb;41(2):285-295. doi: 10.1007/s00296-020-04761-8. Epub 2021 Jan 2. Rheumatol Int. 2021. PMID: 33386899
-
Skin involvement in systemic sclerosis.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008 Oct;47 Suppl 5:v44-5. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ken309. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2008. PMID: 18784142 Review.
Cited by
-
Skin Ultrasound Assessment of Patients with Systemic Scleroderma-An Observational Study.J Pers Med. 2024 Jul 8;14(7):734. doi: 10.3390/jpm14070734. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39063988 Free PMC article.
-
Methods for objective assessment of skin involvement in systemic sclerosis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2023 Nov 1;35(6):301-308. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0000000000000968. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 37605869 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salivary ultrasonography and histopathologic evaluation of secondary Sjögren's syndrome in rheumatoid arthritis patients.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 13;13(1):11339. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-38469-z. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37443200 Free PMC article.
-
The value of shear wave elastography in diagnosis and assessment of systemic sclerosis.Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2023 May 5;7(3):rkad075. doi: 10.1093/rap/rkad075. eCollection 2023. Rheumatol Adv Pract. 2023. PMID: 37711664 Free PMC article.
-
The role of ultrasound in systemic sclerosis: On the cutting edge to foster clinical and research advancement.J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2021 Jun;6(2):123-132. doi: 10.1177/2397198320970394. Epub 2020 Nov 19. J Scleroderma Relat Disord. 2021. PMID: 35386740 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pope JE, Baron M, Bellamy N, Campbell J, et al. Variability of skin scores and clinical measurements in scleroderma. J Rheumatol. 1995;22:1271–1276. - PubMed
-
- Kaldas M, Khanna PP, Furst DE, Clements PJ, et al. Sensitivity to change of the modified Rodnan skin score in diffuse systemic sclerosis--assessment of individual body sites in two large randomized controlled trials. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2009;48:1143–1146. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kep202. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

